Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 35529482
- PMCID: PMC9074886
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.13319
Glucocorticoids induce osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats via PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (SONFH) is a disorder that causes severe disability in patients and has a high incidence worldwide. Although glucocorticoid (GC)-induced apoptosis of osteoblasts is an important cytological basis of SONFH, the detailed mechanism underlying SONFH pathogenesis remains elusive. PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was reported to involve in cell survival and apoptosis.
Objective: We explored the role of PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway and its downstream targets during glucocorticoid -induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head.
Methods: We obtained gene expression profile of osteoblasts subjected to dexamethasone (Dex) treatment from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened out and functional enrichment analysis were conducted by bioinformatics analysis. In vitro, we analyzed Dex-induced apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells and explored the role of PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway in this phenomenon by employing siRNA-FOXO1 and IGF-1(PI3K/AKT agonist). Finally, we verified our results in a rat model of SONFH.
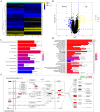
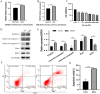
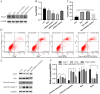
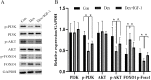
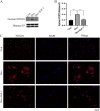
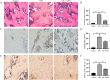
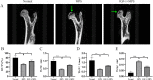
Results: In Dex-treated osteoblasts, DEGs were mainly enriched in the FOXO signaling pathway. Dex inhibited MC3T3-E1 cell viability in a dose-dependent effect and induced apoptosis by increasing the expression levels of FOXO1, Bax, cleaved-Caspase-3, and cleaved-Caspase-9, while reducing the expression of Bcl-2. Notably, these results were reversed by siRNA-FOXO1 treatment. Dex inhibited PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, upregulated FOXO1 expression and increased FOXO1 nuclear translocation, which were reversed by IGF-1. Compared to normal rats, the femoral head of SONFH showed increased expression of FOXO1, increased number of apoptotic cells, and empty osteocytic lacunas, as well as decreased bone tissue content and femoral head integrity. Significantly, the effects of GC-induced SONFH were alleviated following IGF-1 treatment.
Conclusion: Dex induces osteoblast apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Our research offers new insights into the underlying molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis in SONFH and proposes FOXO1 as a therapeutic target for this disease.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Dexamethasone; FOXO1; Glucocorticoids; Osteoblast; PI3K/AKT; SONFH.
©2022 Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Caplan A, Fett N, Rosenbach M, Werth VP, Micheletti RG. Prevention and management of glucocorticoid-induced side effects: a comprehensive review: a review of glucocorticoid pharmacology and bone health. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2017;76(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.01.062. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

