Software Application toward Accessible Hearing Care Assessment: Gap in Noise Test
- PMID: 35529544
- PMCID: PMC9076313
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1112598
Software Application toward Accessible Hearing Care Assessment: Gap in Noise Test
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Software Application toward Accessible Hearing Care Assessment: Gap in Noise Test.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9894189. doi: 10.1155/2023/9894189. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37946921 Free PMC article.
Abstract
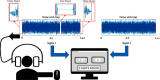
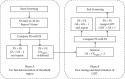
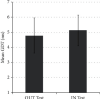
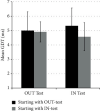
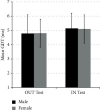
Currently, several methods are being applied to assess auditory temporal resolution in a controlled clinical environment via the measurements of gap detection thresholds (GDTs). However, these methods face two issues: the relatively long time required to perform the gap detection test in such settings and the potential of inaccessibility to such facilities. This article proposes a fast, affordable, and reliable application-based method for the determination of GDT either inside or outside the soundproof booth. The proposed test and the acoustic stimuli were both developed using the MATLAB® programming platform. GDT is determined when the subject is able to distinguish the shortest silent gap inserted randomly in one of two segments of white noise. GDTs were obtained from 42 normal-hearing subjects inside and outside the soundproof booth. The results of this study indicated that average GDTs measured inside the booth (5.12 ± 1.02 ms) and outside (4.78 ± 1.16 ms) were not significantly different. The measured GDTs were also comparable to that reported in the literature. In addition, the GDT screening time of the proposed method was approximately 5 minutes, a screening time that is much less than that reported by the literature. Data show that the proposed application was fast and reliable to screen GDT compared to the standard method currently used in clinical settings.
Copyright © 2022 Khalid Alhussaini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Random Gap Detection Test and Random Gap Detection Test-Expanded results in children with auditory neuropathy.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009 Nov;73(11):1558-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.07.024. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2009. PMID: 19735949
-
The effects of noise vocoding on gap detection thresholds.Cochlear Implants Int. 2015;16(6):331-40. doi: 10.1179/1754762815Y.0000000009. Epub 2015 May 5. Cochlear Implants Int. 2015. PMID: 25941867
-
Behavioral Measures of Temporal Processing and Speech Perception in Cochlear Implant Users.J Am Acad Audiol. 2016 Oct;27(9):701-713. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.15026. J Am Acad Audiol. 2016. PMID: 27718347 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of age and hearing loss on gap detection and the precedence effect: narrow-band stimuli.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2005 Apr;48(2):482-93. doi: 10.1044/1092-4388(2005/033). J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2005. PMID: 15989406
-
Across- and Within-Channel Gap Detection Thresholds Yielded by Two Different Test Applications.J Am Acad Audiol. 2020 Feb;31(2):111-117. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.18099. Epub 2019 Jul 5. J Am Acad Audiol. 2020. PMID: 31287052
Cited by
-
Retracted: Software Application toward Accessible Hearing Care Assessment: Gap in Noise Test.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9894189. doi: 10.1155/2023/9894189. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37946921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deafness and Hearing Loss . World Health Organization; 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss .
-
- Accessibility and Affordability of Hearing Care for Adult Consumers . The American Academy of Audiology; 2017. https://www.audiology.org/practice-resources/practice-guidelines-and-sta... .
-
- Polovoy C. Audiology telepractice overcomes inaccessibility. The ASHA Leader . 2008;13(8):20–22. doi: 10.1044/leader.ftr3.13082008.20. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

