Comparison of the levels of neopterin, CRP, and IL-6 in patients infected with and without SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35529699
- PMCID: PMC9066961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09371
Comparison of the levels of neopterin, CRP, and IL-6 in patients infected with and without SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: Neopterin (NP) is a biomarker for activated cellular immunity and is elevated in diseases including viral and bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases, and cancer. However, the clinical assessment of neopterin has not been used for these disorders because the physiological significance of measuring NP is obscure. It would be important to compare the NP profiles with those of other inflammation markers especially in relatively early phase of patients to reveal the significance of NP measurements in pathological states.
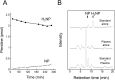
Methods: Plasma NP, biopterin, CRP, and IL-6 levels were measured in 46 patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and 23 patients with non-COVID-19 disorders. The correlations between these markers were analyzed in the COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 patients independently.
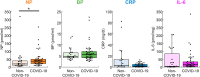
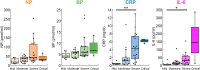
Results: The NP levels were significantly higher in the COVID-19 patients than in the non-COVID-19 patients, while biopterin, CRP and IL-6 were not changed significantly. The NP levels were found to show a weak negative correlation against the days after onset in the COVID-19 patients (rs = -0.348, p = 0.0192), suggesting that the elevation of NP would be an early event of viral infection. Correlations between NP and CRP, or between NP and IL-6 in COVID-19 patients were weaker than that between CRP and IL-6.
Conclusions: The elevation of NP levels was supposed to be distinct from those of CRP and IL-6 in relatively early and mild COVID-19 patients. Our data suggest that NP is produced at the early phase of infection by different signaling pathways and/or cells from those of CRP and IL-6. Further study on the signaling pathway to induce NP is expected.
Keywords: Biomarker; COVID-19; CRP; IL-6; Neopterin; SARS-CoV-2; Viral infection.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hoffmann G., Wirleitner B., Fuchs D. Potential role of immune system activation-associated production of neopterin derivatives in humans. Inflamm. Res. 2003;52(8):313–321. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Vol. 31. 2021. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Situation Report. August.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

