Coronavirus Infection and Cholesterol Metabolism
- PMID: 35529872
- PMCID: PMC9069556
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.791267
Coronavirus Infection and Cholesterol Metabolism
Abstract
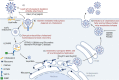
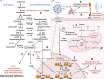
Host cholesterol metabolism remodeling is significantly associated with the spread of human pathogenic coronaviruses, suggesting virus-host relationships could be affected by cholesterol-modifying drugs. Cholesterol has an important role in coronavirus entry, membrane fusion, and pathological syncytia formation, therefore cholesterol metabolic mechanisms may be promising drug targets for coronavirus infections. Moreover, cholesterol and its metabolizing enzymes or corresponding natural products exert antiviral effects which are closely associated with individual viral steps during coronavirus replication. Furthermore, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infections are associated with clinically significant low cholesterol levels, suggesting cholesterol could function as a potential marker for monitoring viral infection status. Therefore, weaponizing cholesterol dysregulation against viral infection could be an effective antiviral strategy. In this review, we comprehensively review the literature to clarify how coronaviruses exploit host cholesterol metabolism to accommodate viral replication requirements and interfere with host immune responses. We also focus on targeting cholesterol homeostasis to interfere with critical steps during coronavirus infection.
Keywords: cholesterol; coronavirus; immune response; metabolism dysregulation; therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Dai, Wang, Liao, Tan, Sun, Song, Liu, Qiu and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of p53-Mediated Host-Virus Interaction in Coronavirus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 28;24(7):6371. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076371. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of the Antiviral Immune Response and Its Circumvention by Coronaviruses.Viruses. 2020 Sep 18;12(9):1039. doi: 10.3390/v12091039. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32961897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MOV10 Helicase Interacts with Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein and Has Antiviral Activity.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0131621. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01316-21. Epub 2021 Sep 14. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34517762 Free PMC article.
-
Virus infection and sphingolipid metabolism.Antiviral Res. 2024 Aug;228:105942. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105942. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 38908521 Review.
-
A Kinome-Wide Small Interfering RNA Screen Identifies Proviral and Antiviral Host Factors in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication, Including Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase and Early Secretory Pathway Proteins.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8318-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01029-15. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26041291 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Intracellular Transcriptional Response of NHBE Cells to Infection with SARS-CoV-2 Washington and New York Strains.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 20;12:1009328. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1009328. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36204651 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of HDL-C on long-term mortality in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the Turkish population: A potential mechanism for population differences.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Oct 23;22(6):1016-1024. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2022.7545. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35997994 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Porcine Deltacoronavirus RNA in the Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract and Biliary Fluid and the Effect of Infection on Serum Cholesterol Levels and Blood T Cell Population Frequencies in Gnotobiotic Piglets.Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 4;10(2):117. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10020117. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36851421 Free PMC article.
-
Kinome and phosphoproteome reprogramming underlies the aberrant immune responses in critically ill COVID-19 patients.Clin Proteomics. 2024 Feb 22;21(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12014-024-09457-w. Clin Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38389037 Free PMC article.
-
Viperin mutation is linked to immunity, immune cell dynamics, and metabolic alteration during VHSV infection in zebrafish.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 19;14:1327749. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1327749. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38173722 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

