Role of Dendritic Cells in Viral Brain Infections
- PMID: 35529884
- PMCID: PMC9072653
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.862053
Role of Dendritic Cells in Viral Brain Infections
Abstract
To gain access to the brain, a so-called immune-privileged organ due to its physical separation from the blood stream, pathogens and particularly viruses have been selected throughout evolution for their use of specific mechanisms. They can enter the central nervous system through direct infection of nerves or cerebral barriers or through cell-mediated transport. Indeed, peripheral lymphoid and myeloid immune cells can interact with the blood-brain and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barriers and allow viral brain access using the "Trojan horse" mechanism. Among immune cells, at the frontier between innate and adaptive immune responses, dendritic cells (DCs) can be pathogen carriers, regulate or exacerbate antiviral responses and neuroinflammation, and therefore be involved in viral transmission and spread. In this review, we highlight an important contribution of DCs in the development and the consequences of viral brain infections.
Keywords: blood–brain barrier; blood–cerebrospinal barrier; dendritic cell; neuroinfections; neuroinflammation; viral infection.
Copyright © 2022 Constant, Maarifi, Blanchet, Van de Perre, Simonin and Salinas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
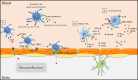
Figures


References
-
- Cassady KA, Whitley RJ. Infections of the Central Nervous System Vol. 44. New York: Lippincott Williams Wilkins; (2004) p. 57–74.
-
- Scheld MW, Whitley RJ, Marra CM. Infections of the Central Nervous System. Philadelphia, Pennsylvannia, USA:Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

