Clinical Efficacy of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium Bromide/Formoterol in the Treatment of Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Its Effect on Inflammatory Factors
- PMID: 35529915
- PMCID: PMC9071865
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8150444
Clinical Efficacy of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium Bromide/Formoterol in the Treatment of Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Its Effect on Inflammatory Factors
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Clinical Efficacy of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium Bromide/Formoterol in the Treatment of Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Its Effect on Inflammatory Factors.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9839030. doi: 10.1155/2023/9839030. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125176 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To examine the clinical efficacy of budesonide/glycopyrronium bromide/formoterol (Breztri Aerosphere) as an adjunct to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Methods: A prospective study enrolled 120 patients with pulmonary endogenous ARDS admitted to the Department of Critical Care Medicine at the Fourth Hospital of Baotou from January 2017 to January 2020, and all enrollments were assigned (1 : 1) to receive conventional treatment (control group) or Breztri Aerosphere (study group).
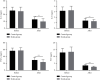
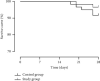
Results: Breztri Aerosphere was associated with a significantly higher total efficacy versus conventional treatment. Breztri Aerosphere resulted in significantly lower acute physiology and chronic health evaluation scoring system (APACHE II) scores and Murray lung injury scores versus conventional treatment. Both groups saw an increase in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2), partial pressure of oxygen (PO2), and oxygen saturation (SaO2) after treatment, with higher levels seen in patients given Breztri Aerosphere. After treatment, systemic vascular resistance (SVR) in both groups rose markedly, with greater elevation witnessed in the study group. The patients given Breztri Aerosphere showed significantly lower levels of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), mean pulmonary arterial pressure (MAPA), pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and procalcitonin (PCT) versus those receiving conventional treatment. The patients experienced shorter mechanical ventilation time and intensive care unit (ICU) time after treatment of Breztri Aerosphere versus conventional treatment.
Conclusion: Adjuvant therapy with Breztri Aerosphere in ARDS can significantly lower APACHE II scores and Murray lung injury scores, improve blood gas indexes and pulmonary circulation function indexes, and shorten mechanical ventilation time and ICU time, which may be attributed to its improvement of organism inflammation status and reduction of inflammatory factors.
Copyright © 2022 Haiying Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Influence of enteral nutrition initiation timing on curative effect and prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome patients with mechanical ventilation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Jun;30(6):573-577. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.06.014. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30009734 Chinese.
-
Risk Factors Analysis of Thoracic Trauma Complicated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Observation of Curative Effect of Lung-Protective Ventilation.Front Surg. 2022 Jan 24;8:826682. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.826682. eCollection 2021. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35141272 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between pulmonary vascular dysfunction and prognosis of patients with acute lung injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Oct;32(10):1221-1225. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200511-00375. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33198868 Chinese.
-
Comparison table: Inhaled corticosteroids for treatment of COPD.Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020 Sep 7;62(1606):e148-e149. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2020. PMID: 32960875 Review. No abstract available.
-
Unsuccessful and Successful Clinical Trials in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Addressing Physiology-Based Gaps.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 30;12:774025. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.774025. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34916959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of budesonide delivered by high-frequency oscillatory ventilation on acute inflammatory response in severe lung injury in adult rabbits.Physiol Res. 2023 Dec 29;72(S5):S509-S521. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935232. Physiol Res. 2023. PMID: 38165755 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Clinical Efficacy of Budesonide/Glycopyrronium Bromide/Formoterol in the Treatment of Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Its Effect on Inflammatory Factors.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9839030. doi: 10.1155/2023/9839030. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chacko B., Peter J. V., Tharyan P., John G., Jeyaseelan L. Pressure-controlled versus volume-controlled ventilation for acute respiratory failure due to acute lung injury (ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . 2015;1(1) doi: 10.1002/14651858.cd008807.pub2.CD008807 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

