Intermittent Hypoxia Inhibits Hepatic CYP1a2 Expression and Delays Aminophylline Metabolism
- PMID: 35529917
- PMCID: PMC9076297
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2782702
Intermittent Hypoxia Inhibits Hepatic CYP1a2 Expression and Delays Aminophylline Metabolism
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we aimed to determine the effects of intermittent hypoxia (IH) on hepatic cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) expression and the pharmacokinetics of CYP1A2-mediated aminophylline and warfarin in vitro and in a rabbit model of obstructive sleep apnea.
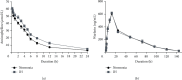
Materials: Human normal liver (LO-2) cells were exposed to 30 min each of 1%, 1-21%, 21%, and 21-1% O2, and then, CYP1A2 expression and drug concentrations were analyzed. We compared the pharmacokinetic parameters of drugs administered to normoxic rabbits and those exposed to 10 min of IH during which the oxygen level fluctuated from 21% to 8%-10% (n = 10 per group).
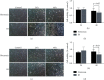
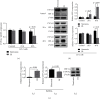
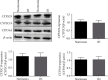
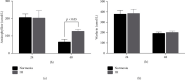
Result: s. The expression of CYP1A2 protein in vitro was significantly reduced in the IH compared with the normoxic cells (0.56 ± 0.11 vs. 1.27 ± 0.17, p < 0.001). Aminophylline was more abundant in cell culture supernatants after 48 h of IH than in those under normoxia. The T 1/2, AUC0-24 h, and Ke values for aminophylline were significantly higher in the IH group.
Conclusion: Intermittent hypoxia inhibits hepatic CYP1A2 expression and delays aminophylline metabolism, suggesting that the impact of IH on the expression of CYP enzymes should be closely monitored in clinical practice.
Copyright © 2022 Xiao-Bin Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fradette C., Du Souich P. Effect of hypoxia on cytochrome P450 activity and expression. Current Drug Metabolism . 2004;5(3):257–271. - PubMed
-
- Fradette C., Batonga J., Teng S., Piquette-Miller M., du Souich P. Animal models of acute moderate hypoxia are associated with a down-regulation of CYP1A1, 1A2, 2B4, 2C5, and 2C16 and up-regulation of CYP3A6 and P-glycoprotein in liver. Drug Metabolism & Disposition . 2007;35(5):765–771. - PubMed
-
- Cumming J. F. The effect of arterial oxygen tension on antipyrine half-time in plasma. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics . 1976;19(4):498–471. - PubMed
-
- Lainscak M., Vitale C., Seferovic P., Spoletini I., Cvan Trobec K., Rosano G. M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cardiovascular drugs in chronic heart failure. International Journal of Cardiology . 2016;224:191–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

