Safety and Effectiveness of Inhaling Different Dosage Recombinant Human Interferon α 1B for Bronchiolitis in Children: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35529920
- PMCID: PMC9068289
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2229735
Safety and Effectiveness of Inhaling Different Dosage Recombinant Human Interferon α 1B for Bronchiolitis in Children: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To systematically evaluate the safety and effectiveness of different dosages of recombinant human interferon α1b (IFNα1b) inhaled for bronchiolitis in children.
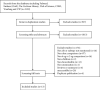
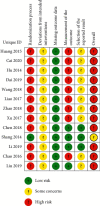
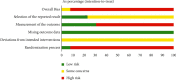
Methods: 7 databases, including PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CNKI, Wanfang Database, and VIP, were searched. The search time was from their inception dates to March 28, 2022. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 2 μg/kg IFNα1b (low dosage group) monotherapy or in combination with other drugs vs. 4 μg/kg IFNα1b (high dosage group) monotherapy or in combination with the other drugs was included. The risk of bias 2.0 evaluated the RCT's quality, and the grading of recommendations assessment, development and evaluation (GRADE) tool was used for evaluating the overall quality of the evidence. Then, a meta-analysis was performed by RevMan 5.4.
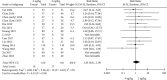
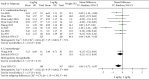
Results: A total of 13 RCTs with 1719 children were included. The meta-analysis results showed that the high dosage group was significantly shorter than the low dosage group of the duration of hospital stays (MD = -0.40, 95%CI (-0.73, -0.07), P = 0.02) (low quality), three depressions sign disappearing time (MD = -0.60, 95%CI (-1.05, -0.14), P = 0.010) (low quality), and wheeze disappearing time (MD = -0.62, 95%CI (-1.17, -0.06), = 0.03) (low quality). There was no significant difference between the two groups in coughing disappearing time, pulmonary rales disappearing time, wheezing sound disappearing time, or adverse event rates.
Conclusions: Compared with low dosage IFNα1b, high dosage IFNα1b reduces the duration of hospital stays, the disappearance time of the three depression signs, and the disappearance time of wheeze in the treatment of bronchiolitis in children. Limited by the low quality of the evidence, the conclusions still need to be supported by high-quality studies.
Copyright © 2022 Jiefeng Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures









References
-
- Merck Clinic Manual[homepage on the Internet]. Bronchiolitis. 2018-08-01; https://www.msdmanuals.cn/professional/pediatrics/respiratory-disorders-....
-
- Liu E., Chen H., Qian Y. Expert consensus on the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of bronchiolitis (2014) Chin J Pediatr . 2015;53(03):168–171.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

