Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Seven Major Compounds in Normal and Atherosclerosis Mice after Oral Administration of Simiao Yong'an Decoction
- PMID: 35529931
- PMCID: PMC9071858
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4604601
Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Seven Major Compounds in Normal and Atherosclerosis Mice after Oral Administration of Simiao Yong'an Decoction
Abstract
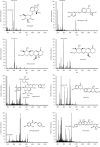
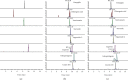
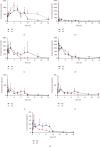
Simiao Yong'an decoction (SMYAD), a classic traditional Chinese medicine formula, has been used to treat atherosclerosis (AS) in clinical in China, but its therapeutic mechanism and pharmacodynamic material basis are not clear. In this study, the AS model was caused by a high-fat diet and perivascular carotid collar placement (PCCP), and SMYAD was orally administered to the model and normal mice. A rapid, sensitive, selective, and reliable method using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) system combined with a Q Exactive HF-X mass spectrometer (UHPLC-Q Exactive HF-X MS) was established and validated for the simultaneous determination of seven compounds, including harpagide, chlorogenic acid, swertiamarin, sweroside, angoroside C, liquiritin, and isoliquiritigenin in the plasma of normal and AS mice. The specificity, linearity, precision, accuracy, recovery, and stability of the method were all within the acceptable criteria. The results showed that some pharmacokinetic behaviors of harpagide, chlorogenic acid, and isoliquiritigenin were significantly different among the two groups of mice. The specific parameter changes were harpagide (AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ were 11075.09 ± 2132.38 and 16221.95 ± 5622.42 ng·mL-1·h, respectively; CLz/F was 2.45 ± 0.87 L/h/mg), chlorogenic acid (t 1/2 was 21.59 ± 9.16 h; AUC0-∞ was 2637.51 ± 322.54 ng·mL-1·h; CLz/F was 13.49 ± 1.81 L/h/mg) and isoliquiritigenin (AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ were 502.25 ± 165.65 and 653.68 ± 251.34 ng·mL-1·h, respectively; CLz/F was 62.16 ± 23.35 L/h/mg) were altered under the pathological status of AS. These differences might be partly ascribed to the changes in gastrointestinal microbiota, nonspecific drug transporters, and cytochrome P450 activity under the AS state, providing research ideas and experimental basis for pharmacological effects and pharmacodynamic material basis.
Copyright © 2022 Ke-han Sun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Arnett D. K., Blumenthal R. S., Albert M. A., et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: executive summary: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2019;74(10):1376–1414. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.03.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

