Impact of deoxynivalenol and kaempferol on expression of tight junction proteins at different stages of Caco-2 cell proliferation and differentiation
- PMID: 35529998
- PMCID: PMC9073856
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06222j
Impact of deoxynivalenol and kaempferol on expression of tight junction proteins at different stages of Caco-2 cell proliferation and differentiation
Abstract
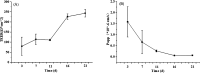
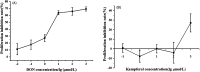
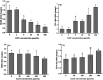
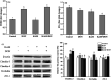
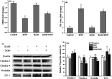
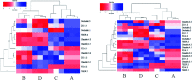
The barrier function of intestinal tract is essential to gut health, and the expression of tight junction (TJ) proteins in human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells, mimicking the intestinal stem cell proliferation and differentiation, was investigated after treatment by the mycotoxin of deoxynivalenol (DON) and phenolic compound of kaempferol (KAM). The results showed that DON (5 μM) significantly reduced the expression of claudin-4 while kaempferol (100 μM) increased the expression of claudin-3 during Caco-2 cell proliferation. After being cultured for 11 days, the DON treatment, unexpectedly, augmented the expression of claudin-4 with an increased TEER. For differentiated Caco-2 cells after a 21 day culture, both the TEER and claudin-4 levels were significantly reduced by DON while KAM pretreatment alleviated the damage caused by DON accompanying an increase of TEER, claudin-3, and ZO-1. Thus, kaempferol and DON differentially affected the expression of tight junction proteins at different stages of Caco-2 cell proliferation and differentiation, and an increase of the integrity of TJ after KAM pretreatment indicates KAM has the potential to protect the integrity of the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium for improved health.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Critical Review of Kaempferol in Intestinal Health and Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 20;12(8):1642. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081642. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of deoxynivalenol-induced endocytosis and degradation of tight junction proteins in jejunal IPEC-J2 cells involve selective activation of the MAPK pathways.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Jun;95(6):2065-2079. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03044-w. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33847777
-
A proteomic study on the protective effect of kaempferol pretreatment against deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction in a Caco-2 cell model.Food Funct. 2020 Aug 1;11(8):7266-7279. doi: 10.1039/d0fo01579b. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32776049
-
EPA and DHA inhibit endocytosis of claudin-4 and protect against deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal barrier dysfunction through PPARγ dependent and independent pathways in jejunal IPEC-J2 cells.Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111420. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111420. Epub 2022 May 27. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35761666
-
Vulnerability of polarised intestinal porcine epithelial cells to mycotoxin deoxynivalenol depends on the route of application.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 25;6(2):e17472. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017472. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21364771 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exposure to the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol reduces the transport of conjugated bile acids by intestinal Caco-2 cells.Arch Toxicol. 2022 May;96(5):1473-1482. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03256-8. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35224661 Free PMC article.
-
Mycotoxins: Biotransformation and Bioavailability Assessment Using Caco-2 Cell Monolayer.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 30;12(10):628. doi: 10.3390/toxins12100628. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33008111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional and emerging Fusarium mycotoxins disrupt homeostasis of bovine mammary cells by altering cell permeability and innate immune function.Anim Nutr. 2022 Dec 1;12:388-397. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.10.007. eCollection 2023 Mar. Anim Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36733782 Free PMC article.
-
A Critical Review of Kaempferol in Intestinal Health and Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 20;12(8):1642. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081642. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627637 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ochratoxin A and Citrinin Differentially Modulate Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cell Permeability and Innate Immune Function.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 16;14(9):640. doi: 10.3390/toxins14090640. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36136578 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

