The Influence of Serum Uric Acid on the Brain and Cognitive Dysfunction
- PMID: 35530021
- PMCID: PMC9072620
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.828476
The Influence of Serum Uric Acid on the Brain and Cognitive Dysfunction
Abstract
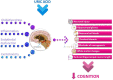
Uric acid is commonly known for its bad reputation. However, it has been shown that uric acid may be actively involved in neurotoxicity and/or neuroprotection. These effects could be caused by oxidative stress or inflammatory processes localized in the central nervous system, but also by other somatic diseases or systemic conditions. Our interest was to summarize and link the current data on the possible role of uric acid in cognitive functioning. We also focused on the two putative molecular mechanisms related to the pathological effects of uric acid-oxidative stress and inflammatory processes. The hippocampus is a prominent anatomic localization included in expressing uric acid's potential impact on cognitive functioning. In neurodegenerative and mental disorders, uric acid could be involved in a variety of ways in etiopathogenesis and clinical presentation. Hyperuricemia is non-specifically observed more frequently in the general population and after various somatic illnesses. There is increasing evidence to support the hypothesis that hyperuricemia may be beneficial for cognitive functioning because of its antioxidant effects but may also be a potential risk factor for cognitive dysfunction, in part because of increased inflammatory activity. In this context, gender specificities must also be considered.
Keywords: cognition; inflammation; neuroprotection; neurotoxicity; oxidative stress; uric acid.
Copyright © 2022 Mijailovic, Vesic and Borovcanin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detrimental effects of long-term elevated serum uric acid on cognitive function in rats.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 24;11(1):6732. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86279-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33762656 Free PMC article.
-
Uric Acid and Cognitive Function in Older Individuals.Nutrients. 2018 Jul 27;10(8):975. doi: 10.3390/nu10080975. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30060474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uric Acid Induces Cognitive Dysfunction through Hippocampal Inflammation in Rodents and Humans.J Neurosci. 2016 Oct 26;36(43):10990-11005. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1480-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27798180 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid: friend or foe? Uric acid and cognitive function "Gout kills more wise men than simple".Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Feb;19(4):640-6. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25753882 Review.
-
Lower uric Acid linked with cognitive dysfunction in the elderly.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015;14(5):564-6. doi: 10.2174/1871527314666150430161659. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2015. PMID: 25925000
Cited by
-
Establishment, Prediction, and Validation of a Nomogram for Cognitive Impairment in Elderly Patients With Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Aug 19;2024:5583707. doi: 10.1155/2024/5583707. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39188897 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting uric acid: a promising intervention against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jan 3;23(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01965-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39754256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the relationship between the uric acid to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and depression: a cross-sectional study from NHANES.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):32018. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83655-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738694 Free PMC article.
-
Role of uric acid in neurodegenerative diseases, focusing on Alzheimer and Parkinson disease: A new perspective.Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2024 Sep;44(3):639-649. doi: 10.1002/npr2.12445. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39075837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between the serum uric acid/serum creatinine ratio and cognitive function in older adults: NHANES in the United States.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 15;14(1):16312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67580-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39009809 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

