Comparison of Students' Mental Wellbeing, Anxiety, Depression, and Quality of Life During COVID-19's Full and Partial (Smart) Lockdowns: A Follow-Up Study at a 5-Month Interval
- PMID: 35530024
- PMCID: PMC9067378
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.835585
Comparison of Students' Mental Wellbeing, Anxiety, Depression, and Quality of Life During COVID-19's Full and Partial (Smart) Lockdowns: A Follow-Up Study at a 5-Month Interval
Abstract
Objective: Scholars have debated the COVID-19's full and partial lockdowns' effectivity to control the transmission of the new case. They emphasized the provision of required economic and social resources worldwide. Past literature related to COVID-19 has contributed little evidence to examine the efficacy of full and partial lockdown measures with experimental perspectives at different intervals. This study bridges this literature gap and explores the full and smart lockdowns' impacts on Pakistani students' mental health, depression, quality of life, and anxiety symptoms, during the various waves of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Method: This pretest and posttest experimental designed web-based survey recruited 40 students from March 23 to August 23, 2020, and recorded their responses. The study incorporated four standardized psychological instruments to receive the desired datasets related to students' mental health, quality of life, anxiety, and depression. Researchers shared data links with the participants via social media, WhatsApp. The study applied one-way and multivariate ANOVA tests (analysis of variance) to draw the desired results.
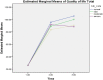
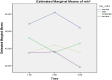
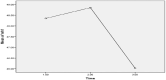
Results: This study's findings suggest that both full and partial COVID-19 lockdowns effectively improve students' mental health and quality of life. These measures help reduce anxiety and depressive symptoms among university students. The study results exhibit that partial lockdown (PL) is more effective in improving quality of life. Besides, PL helps reduce anxiety symptoms than complete lockdown among Pakistani students.
Conclusion: The present study's findings suggest that students are vulnerable. They need particular interventions and preventive measures to protect and improve their mental health and quality of life during a global pandemic. As the stressful experience of the epidemic persists in Pakistan. It will also be interesting to examine the psychological impact of the successive waves of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19 full lockdown; COVID-19 preventive health behavior; anxiety; depression; mental health; quality of life; smart lockdown.
Copyright © 2022 Aqeel, Rehna, Shuja and Abbas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Lockdown in Chinese university dormitories: Significant increase in negative feelings and time perception distortion.Psychol Sch. 2022 Dec 1:10.1002/pits.22833. doi: 10.1002/pits.22833. Online ahead of print. Psychol Sch. 2022. PMID: 36718134 Free PMC article.
-
The Positive Effect of Video-Game Play on College Students' Anxiety and Depression Symptoms During the COVID-19 Pandemic Shelter-in-Place Lockdowns: Mixed Methods Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2025 May 30;13:e58857. doi: 10.2196/58857. JMIR Serious Games. 2025. PMID: 40446291 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation between lifestyle health behaviors, coping style, and mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic among college students: Two rounds of a web-based study.Front Public Health. 2023 Jan 12;10:1031560. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1031560. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36711327 Free PMC article.
-
Yoga and meditation, an essential tool to alleviate stress and enhance immunity to emerging infections: A perspective on the effect of COVID-19 pandemic on students.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 Mar;20:100420. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100420. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 35072120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
For the Greater Good? The Devastating Ripple Effects of the Covid-19 Crisis.Front Psychol. 2020 Sep 29;11:577740. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.577740. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 33132987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of various geological factors on the real estate valuation using AHP analysis: case studies from Turkey.Environ Dev Sustain. 2023 Feb 11:1-17. doi: 10.1007/s10668-023-03008-3. Online ahead of print. Environ Dev Sustain. 2023. PMID: 36817738 Free PMC article.
-
Mediation effects of post-series depression on the relationship between life satisfaction and positive mental health of Vietnamese: A cross-sectional study in COVID-19 pandemic context.Front Psychol. 2022 Nov 28;13:971711. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.971711. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36518965 Free PMC article.
-
From Cultural Tourism to Social Entrepreneurship: Role of Social Value Creation for Environmental Sustainability.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 4;13:925768. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.925768. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35911048 Free PMC article.
-
Postpartum post-traumatic stress symptoms during the COVID-19 period: exposure and fear as mediating factors.Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2023;14(2):2228151. doi: 10.1080/20008066.2023.2228151. Eur J Psychotraumatol. 2023. PMID: 37534932 Free PMC article.
-
Scientists' deficit perception of the public impedes their behavioral intentions to correct misinformation.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 2;18(8):e0287870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287870. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37531388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elena C, Rosa VLL, Giulia C, Parisi J. The psychological impact of the lockdown on Italian university students during the first wave of COVID-19 pandemic: psychological experiences, health risk perceptions, distance learning, and future perspectives. Mediterranean J Clin Psychol. (2020) 9:1–19. 10.13129/2282-1619/mjcp-3009 - DOI
-
- Ghebreyesus TA. World Health Organization. WHO Director-General's Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-25 May 2020 (2020)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

