Tensile mechanical performance of Ni-Co alloy nanowires by molecular dynamics simulation
- PMID: 35530058
- PMCID: PMC9070038
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04294f
Tensile mechanical performance of Ni-Co alloy nanowires by molecular dynamics simulation
Abstract
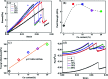
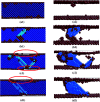
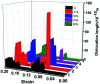
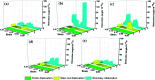
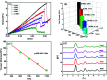
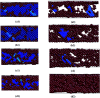
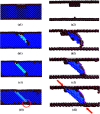
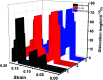
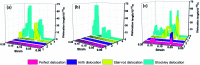
In this present contribution, tensile mechanical properties of Ni-Co alloy nanowires with Co content from 0 to 20% were studied by molecular dynamics. The simulation results show the alloy nanowire with the Co content of 5% has the highest yield value of 9.72 GPa. In addition, more Frank dislocations were generated during the loading process to improve the performance of the alloy nanowire. The Young's modulus increases little by little from 105.68 to 179.78 GPa with the increase of Co content. Secondly, with the increase of temperature, the yield strength gradually decreases to 2.13 GPa. Young's modulus tends to decrease linearly from 170.7 GPa to 48.21 GPa. At the temperatures of 500 K and 700 K, it is easier to form Frank dislocation and Hirth dislocation, respectively, in the loading process. The peak value of the radial distribution function decreases and the number of peaks decreases, indicating the disappearance of the ordered structure. Finally, after the introduction of the surface and inner void, the yield strength of the nanowire drops about to 8.97 and 6.6 GPa, respectively, and the yield strains drop to 0.056 and 0.043. In the case of the existence of internal void, perfect dislocation and Hirth dislocation can be observed in the structure.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A molecular dynamics study on the mechanical properties of Fe-Ni alloy nanowires and their temperature dependence.RSC Adv. 2020 Nov 3;10(66):40084-40091. doi: 10.1039/d0ra07831j. eCollection 2020 Nov 2. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35520820 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical characterization of Co/Cu multilayered nanowires.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012 Jun;12(6):4710-6. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2012.4896. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22905520
-
Investigation on mechanical behaviors of Cu-Ni binary alloy nanopillars: a molecular dynamics study.J Mol Model. 2020 Jul 24;26(8):214. doi: 10.1007/s00894-020-04440-2. J Mol Model. 2020. PMID: 32705399
-
Effect of Void Defects on the Indentation Behavior of Ni/Ni3Al Crystal.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;13(13):1969. doi: 10.3390/nano13131969. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37446485 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the deformation behavior and mechanical characteristics of polycrystalline chromium-nickel alloys using molecular dynamics.J Mol Model. 2022 Sep 22;28(10):328. doi: 10.1007/s00894-022-05321-6. J Mol Model. 2022. PMID: 36138158
Cited by
-
The impact of alloying on defect-free nanoparticles exhibiting softer but tougher behavior.Nat Commun. 2021 May 4;12(1):2515. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22707-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33947860 Free PMC article.
-
Atomistic Construction of Silicon Nitride Ceramic Fiber Molecular Model and Investigation of Its Mechanical Properties Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Materials (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;16(18):6082. doi: 10.3390/ma16186082. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Y. Yang H. Liu Y. Jiang B. Woodward R. Acta Mater. 2005;53:3625. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.04.019. - DOI
-
- Nishida R. Puengjinda P. Nishino H. RSC Adv. 2014;4:16260. doi: 10.1039/C3RA47089J. - DOI
-
- Yang C. L. Zhang Z. J. Zhang P. Cui C. Y. Zhang Z. F. Mater. Sci. Eng., A. 2018;736:100. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.012. - DOI
-
- Habibi B. Delnavaz N. RSC Adv. 2016;6:31797. doi: 10.1039/C5RA26006J. - DOI
-
- Wang L. Gao Y. Xue Q. Liu H. Xu T. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005;242:326. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2004.08.033. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

