Remembering your A, B, C's: Alzheimer's disease and ABCA1
- PMID: 35530134
- PMCID: PMC9072248
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2022.01.011
Remembering your A, B, C's: Alzheimer's disease and ABCA1
Abstract
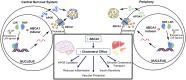
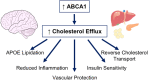
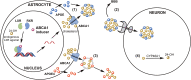
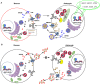
The function of ATP binding cassette protein A1 (ABCA1) is central to cholesterol mobilization. Reduced ABCA1 expression or activity is implicated in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other disorders. Therapeutic approaches to boost ABCA1 activity have yet to be translated successfully to the clinic. The risk factors for AD development and progression, including comorbid disorders such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, highlight the intersection of cholesterol transport and inflammation. Upregulation of ABCA1 can positively impact APOE lipidation, insulin sensitivity, peripheral vascular and blood-brain barrier integrity, and anti-inflammatory signaling. Various strategies towards ABCA1-boosting compounds have been described, with a bias toward nuclear hormone receptor (NHR) agonists. These agonists display beneficial preclinical effects; however, important side effects have limited development. In particular, ligands that bind liver X receptor (LXR), the primary NHR that controls ABCA1 expression, have shown positive effects in AD mouse models; however, lipogenesis and unwanted increases in triglyceride production are often observed. The longstanding approach, focusing on LXRβ vs. LXRα selectivity, is over-simplistic and has failed. Novel approaches such as phenotypic screening may lead to small molecule NHR modulators that elevate ABCA1 function without inducing lipogenesis and are clinically translatable.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Cardiovascular disease; Cholesterol; Drug discovery; Liver X receptor; Nuclear hormone receptor; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s A. 2020 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2020;16:391–460.
-
- Alzheimer's A. 2016 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12:459–509. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

