Structure-guided discovery of potent and oral soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors for the treatment of neuropathic pain
- PMID: 35530144
- PMCID: PMC9072249
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.018
Structure-guided discovery of potent and oral soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors for the treatment of neuropathic pain
Abstract
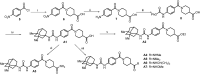
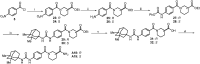
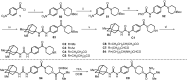
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is related to arachidonic acid cascade and is over-expressed in a variety of diseases, making sEH an attractive target for the treatment of pain as well as inflammatory-related diseases. A new series of memantyl urea derivatives as potent sEH inhibitors was obtained using our previous reported compound 4 as lead compound. A preferential modification of piperidinyl to 3-carbamoyl piperidinyl was identified for this series via structure-based rational drug design. Compound A20 exhibited moderate percentage plasma protein binding (88.6%) and better metabolic stability in vitro. After oral administration, the bioavailability of A20 was 28.6%. Acute toxicity test showed that A20 was well tolerated and there was no adverse event encountered at dose of 6.0 g/kg. Inhibitor A20 also displayed robust analgesic effect in vivo and dose-dependently attenuated neuropathic pain in rat model induced by spared nerve injury, which was better than gabapentin and sEH inhibitor (±)-EC-5026. In one word, the oral administration of A20 significantly alleviated pain and improved the health status of the rats, demonstrating that A20 was a promising candidate to be further evaluated for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Analgesia; Inhibitor; Neuropathic pain; Soluble epoxide hydrolase; Synthesis.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
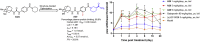
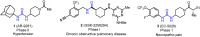


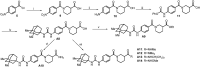








References
-
- Treede R.D., Jensen T.S., Campbell J.N., Cruccu G., Dostrovsky J.O., Griffin J.W., et al. Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008;70:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Bouhassira D. Neuropathic pain: definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2019;175:16–25. - PubMed
-
- van Hecke O., Austin S.K., Khan R.A., Smith B.H., Torrance N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain. 2014;155:654–662. - PubMed
-
- Baron R., Binder A., Wasner G. Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:807–819. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

