WSB1 regulates c-Myc expression through β-catenin signaling and forms a feedforward circuit
- PMID: 35530152
- PMCID: PMC9072231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.10.021
WSB1 regulates c-Myc expression through β-catenin signaling and forms a feedforward circuit
Abstract
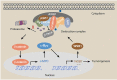
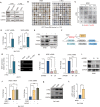
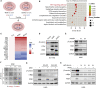
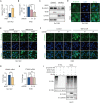
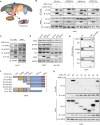
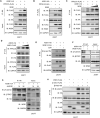
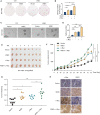
The dysregulation of transcription factors is widely associated with tumorigenesis. As the most well-defined transcription factor in multiple types of cancer, c-Myc can transform cells by transactivating various downstream genes. Given that there is no effective way to directly inhibit c-Myc, c-Myc targeting strategies hold great potential for cancer therapy. In this study, we found that WSB1, which has a highly positive correlation with c-Myc in 10 cancer cell lines and clinical samples, is a direct target gene of c-Myc, and can positively regulate c-Myc expression, which forms a feedforward circuit promoting cancer development. RNA sequencing results from Bel-7402 cells confirmed that WSB1 promoted c-Myc expression through the β-catenin pathway. Mechanistically, WSB1 affected β-catenin destruction complex-PPP2CA assembly and E3 ubiquitin ligase adaptor β-TRCP recruitment, which inhibited the ubiquitination of β-catenin and transactivated c-Myc. Of interest, the effect of WSB1 on c-Myc was independent of its E3 ligase activity. Moreover, overexpressing WSB1 in the Bel-7402 xenograft model could further strengthen the tumor-driven effect of c-Myc overexpression. Thus, our findings revealed a novel mechanism involved in tumorigenesis in which the WSB1/c-Myc feedforward circuit played an essential role, highlighting a potential c-Myc intervention strategy in cancer treatment.
Keywords: ATM, serine-protein kinase ATM; CHIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; CK1, casein kinase 1; Cancer treatment; EBP2, probable rRNA-processing protein EBP2; ESC complex, elongin B/C-cullin 2/5-SOCS box containing ubiquitin ligase protein complex; Feedback loop; GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HIF1-α, hypoxia induced factor 1-alpha; IHC, immunohistochemistry; PLK1, serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK1; PP2A, serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A; PROTAC, proteolysis targeting chimaera; RhoGDI2, Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor 2; TFs, transcription factors; Transcription factors; Tumorigenesis; Ubiquitination-proteasome pathway; WSB1; WSB1, WD repeat and SOCS box containing 1; c-Myc; c-Myc, proto-oncogene c-Myc; eIF4F, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F; β-Catenin destruction complex.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Maston G.A., Evans S.K., Green M.R. Transcriptional regulatory elements in the human genome. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet. 2006;7:29–59. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Nunez V., Rodríguez R.E. In: The neuroscience of cocaine. Preedy V.R., editor. Academic Press; San Diego: 2017. Chapter 12-cocaine and transcription factors; pp. 107–124.
-
- Darnell J.E. Jr. Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:740–749. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

