Chiral mesoporous silica nano-screws as an efficient biomimetic oral drug delivery platform through multiple topological mechanisms
- PMID: 35530160
- PMCID: PMC9072246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.08.014
Chiral mesoporous silica nano-screws as an efficient biomimetic oral drug delivery platform through multiple topological mechanisms
Abstract
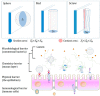
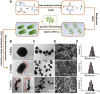
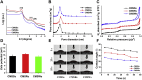
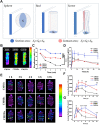
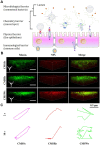
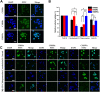
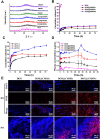
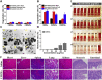
In the microscale, bacteria with helical body shapes have been reported to yield advantages in many bio-processes. In the human society, there are also wisdoms in knowing how to recognize and make use of helical shapes with multi-functionality. Herein, we designed atypical chiral mesoporous silica nano-screws (CMSWs) with ideal topological structures (e.g., small section area, relative rough surface, screw-like body with three-dimension chirality) and demonstrated that CMSWs displayed enhanced bio-adhesion, mucus-penetration and cellular uptake (contributed by the macropinocytosis and caveolae-mediated endocytosis pathways) abilities compared to the chiral mesoporous silica nanospheres (CMSSs) and chiral mesoporous silica nanorods (CMSRs), achieving extended retention duration in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and superior adsorption in the blood circulation (up to 2.61- and 5.65-times in AUC). After doxorubicin (DOX) loading into CMSs, DOX@CMSWs exhibited controlled drug release manners with pH responsiveness in vitro. Orally administered DOX@CMSWs could efficiently overcome the intestinal epithelium barrier (IEB), and resulted in satisfactory oral bioavailability of DOX (up to 348%). CMSWs were also proved to exhibit good biocompatibility and unique biodegradability. These findings displayed superior ability of CMSWs in crossing IEB through multiple topological mechanisms and would provide useful information on the rational design of nano-drug delivery systems.
Keywords: APTES, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane; AR, aspect ratio; AUC0‒∞, area under the curve; CMSRs, chiral mesoporous silica nanorods; CMSSs, chiral mesoporous silica nanospheres; CMSWs, chiral mesoporous silica nano-screws; CMSs, chiral mesoporous silicas nanoparticles; Cd, drug loading capacity; Chiral mesoporous silica; Cmax, maximum concentration; DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DCM, dichloromethane; DOX, doxorubicin; EDC·HCl, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride; FBS, fetal bovine serum; FITC, Fluorescein isothiocyanate; Frel, relative bioavailability; GI, gastrointestinal; Geometric topological structure; HOBT, 1-hydroxybenzotriazole; IEB, intestinal epithelium barrier; IR, infrared spectroscopy; Intestinal epithelium barrier; MRT0‒∞, mean residence time; MSNs, mesoporous silica nanoparticles; Morphology; Mβ-CD, methyl-β-cyclodextrin; N-PLA, N-palmitoyl-l-alanine; NPs, nanoparticles; Nano-screw; Oral adsorption; PBS, phosphate buffer solution; RBCs, red blood cells; RITC, rhodamine B isothiocyanate; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; SBET, Specific surface area; SBF, simulated body fluid; SD, Sprague–Dawley; SGF, simulated gastric fluid; SIF, simulated intestinal fluid; TEOS, ethylsilicate; Tmax, peak time; Vt, pore volume; WBJH, pore diameter; XRD, X-ray diffractometry; nano-DDS, nano-drug delivery systems; t1/2, half-life.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multichiral Mesoporous Silica Screws with Chiral Differential Mucus Penetration and Mucosal Adhesion for Oral Drug Delivery.ACS Nano. 2024 Jun 25;18(25):16166-16183. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c01245. Epub 2024 Jun 12. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38867485
-
Design and preparation of mesoporous silica carriers with chiral structures for drug release differentiation.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Oct;103:109737. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.109737. Epub 2019 May 10. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31349514
-
Mesoporous silica nanorods for improved oral drug absorption.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;46(6):1132-1140. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1362414. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28783976
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 Mar;8(2):165-177. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29719777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Red blood cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles: a novel drug delivery system for antitumor application.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019 Jul;9(4):675-689. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2019.01.011. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2019. PMID: 31384529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biosilicification-mimicking chiral nanostructures for targeted treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 15;16(1):2551. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57890-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40089457 Free PMC article.
-
Mucus interaction to improve gastrointestinal retention and pharmacokinetics of orally administered nano-drug delivery systems.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Aug 6;20(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01539-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35933341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug delivery systems based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the management of hepatic diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Feb;15(2):809-833. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.015. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40177563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of nanovaccine in anti-tumor immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 24;13:1211262. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1211262. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37692854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 24;14(1):7694. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43465-y. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38001086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hristov D., McCartney F., Beirne J., Mahon E., Reid S., Bhattacharjee S., et al. Silica-coated nanoparticles with a core of zinc, l-arginine, and a peptide designed for oral delivery. ACS Appl Mater Inter. 2020;12:1257–1269. - PubMed
-
- Wu X., Qiu H., Che S. Controlling the pitch length of helical mesoporous silica (HMS) Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009;120:294–303.
-
- Jin H., Liu Z., Ohsuna T., Terasaki O., Inoue Y., Sakamoto K., et al. Control of morphology and helicity of chiral mesoporous silica. Adv Mater. 2006;18:593–596.
-
- Choonara B.F., Choonara Y.E., Kumar P., Bijukumar D., du Toit L.C., Pillay V. A review of advanced oral drug delivery technologies facilitating the protection and absorption of protein and peptide molecules. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32:1269–1282. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

