Targeting PFKL with penfluridol inhibits glycolysis and suppresses esophageal cancer tumorigenesis in an AMPK/FOXO3a/BIM-dependent manner
- PMID: 35530161
- PMCID: PMC9069409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.007
Targeting PFKL with penfluridol inhibits glycolysis and suppresses esophageal cancer tumorigenesis in an AMPK/FOXO3a/BIM-dependent manner
Abstract
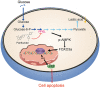
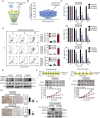
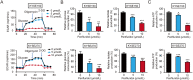
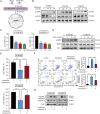
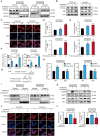
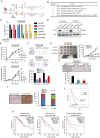
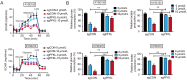
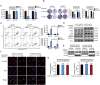
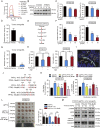
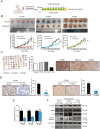
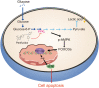
As one of the hallmarks of cancer, metabolic reprogramming leads to cancer progression, and targeting glycolytic enzymes could be useful strategies for cancer therapy. By screening a small molecule library consisting of 1320 FDA-approved drugs, we found that penfluridol, an antipsychotic drug used to treat schizophrenia, could inhibit glycolysis and induce apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Gene profiling and Ingenuity Pathway Analysis suggested the important role of AMPK in action mechanism of penfluridol. By using drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS) technology and proteomics, we identified phosphofructokinase, liver type (PFKL), a key enzyme in glycolysis, as a direct target of penfluridol. Penfluridol could not exhibit its anticancer property in PFKL-deficient cancer cells, illustrating that PFKL is essential for the bioactivity of penfluridol. High PFKL expression is correlated with advanced stages and poor survival of ESCC patients, and silencing of PFKL significantly suppressed tumor growth. Mechanistically, direct binding of penfluridol and PFKL inhibits glucose consumption, lactate and ATP production, leads to nuclear translocation of FOXO3a and subsequent transcriptional activation of BIM in an AMPK-dependent manner. Taken together, PFKL is a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in ESCC, and penfluridol may be a new therapeutic option for management of this lethal disease.
Keywords: DARTS technology; Drug repurposing; Esophageal cancer; Glycolysis; Metabolic reprogramming; PFKL; Penfluridol.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

