Emerging role of natural products in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 35530162
- PMCID: PMC9069318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.08.020
Emerging role of natural products in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
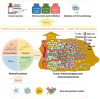
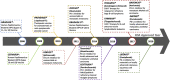
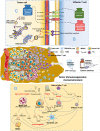
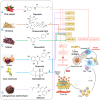
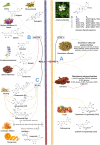
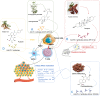
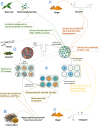
Cancer immunotherapy has become a new generation of anti-tumor treatment, but its indications still focus on several types of tumors that are sensitive to the immune system. Therefore, effective strategies that can expand its indications and enhance its efficiency become the key element for the further development of cancer immunotherapy. Natural products are reported to have this effect on cancer immunotherapy, including cancer vaccines, immune-check points inhibitors, and adoptive immune-cells therapy. And the mechanism of that is mainly attributed to the remodeling of the tumor-immunosuppressive microenvironment, which is the key factor that assists tumor to avoid the recognition and attack from immune system and cancer immunotherapy. Therefore, this review summarizes and concludes the natural products that reportedly improve cancer immunotherapy and investigates the mechanism. And we found that saponins, polysaccharides, and flavonoids are mainly three categories of natural products, which reflected significant effects combined with cancer immunotherapy through reversing the tumor-immunosuppressive microenvironment. Besides, this review also collected the studies about nano-technology used to improve the disadvantages of natural products. All of these studies showed the great potential of natural products in cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: AKT, alpha-serine/threonine-specific protein kinase; Adoptive immune-cells transfer immunotherapy; B2M, beta-2-microglobulin; BMDCs, bone marrow dendritic cells; BPS, basil polysaccharide; BTLA, B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; CCL22, C–C motif chemokine 22; CIKs, cytokine-induced killer cells; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; CRC, colorectal cancer; CTL, cytotoxic T cell; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4; Cancer immunotherapy; Cancer vaccines; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; DCs, dendritic cells; FDA, US Food and Drug Administration; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HER-2, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; HMGB1, high-mobility group box 1; HSPs, heat shock proteins; ICD, Immunogenic cell death; ICTs, immunological checkpoints; IFN-γ, interferon γ; IL-10, interleukin-10; Immuno-check points; Immunosuppressive microenvironment; LLC, Lewis lung cancer; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MHC, major histocompatibility complex class; MITF, melanogenesis associated transcription factor; MMP-9, matrix metalloprotein-9; Mcl-1, myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NKTs, natural killer T cells; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; Natural products; OVA, ovalbumin; PD-1, programmed death-1; PD-L1, programmed death receptor ligand 1; PGE-2, prostaglandin E2; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; TAP, transporters related with antigen processing; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TILs, tumor infiltration lymphocytes; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; TSA, tumor specific antigens; Teffs, effective T cells; Th1, T helper type 1; Tregs, regulatory T cells; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; mTOR, mechanistic target of rapamycin.
© 2022 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Biological drug and drug delivery-mediated immunotherapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Apr;11(4):941-960. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.12.018. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33996408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinically feasible approaches to potentiating cancer cell-based immunotherapies.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015;11(4):851-69. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1009814. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25933181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 26;6(7):1973-1987. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010. eCollection 2021 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33426371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic gene modified cell based cancer vaccines.Gene. 2013 Aug 10;525(2):200-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.03.056. Epub 2013 Apr 6. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23566846 Review.
-
Application of PD-1 Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019 May 23;17:661-674. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.03.006. eCollection 2019. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019. PMID: 31205619 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Emerging Pathogenic Mechanisms by Natural Molecules as Potential Therapeutics for Neurodegenerative Diseases.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 25;14(11):2287. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112287. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of fine-tuning parameters of convolutional neural network for skin cancer detection.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 28;15(1):14779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-99529-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40295678 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying and validating immunological biomarkers in obstructive sleep apnea through bioinformatics analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9746. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93915-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40118992 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using cordycepin and Cordyceps militaris extract to sensitize cancer cells and modulate immune responses.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 19;14(1):21907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72833-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39300166 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products Induce Different Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in Murine Models of 4T1 Mammary Carcinoma and B16-F10 Melanoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 24;24(23):16698. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316698. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hargadon K.M., Johnoson C.E., Williams C.J. Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for cancer: an overview of FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;62:29–39. - PubMed
-
- O'Leary M.C., Lu X., Huang Y., Lin X., Mahmood I., Przepiorka D., et al. FDA approval summary: tisagenlecleucel for treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:1142–1146. - PubMed
-
- Bouchkouj N., Kasamon Y.L., de Claro R.A., George B., Lin X., Lee S., et al. FDA approval summary: axicabtagene ciloleucel for relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:1702–1708. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

