Plasma Proteomics of COVID-19-Associated Cardiovascular Complications: Implications for Pathophysiology and Therapeutics
- PMID: 35530264
- PMCID: PMC9067411
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.01.013
Plasma Proteomics of COVID-19-Associated Cardiovascular Complications: Implications for Pathophysiology and Therapeutics
Abstract
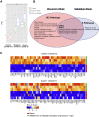
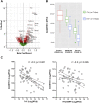
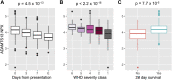
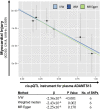
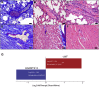
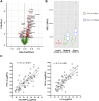
To gain insights into the mechanisms driving cardiovascular complications in COVID-19, we performed a case-control plasma proteomics study in COVID-19 patients. Our results identify the senescence-associated secretory phenotype, a marker of biological aging, as the dominant process associated with disease severity and cardiac involvement. FSTL3, an indicator of senescence-promoting Activin/TGFβ signaling, and ADAMTS13, the von Willebrand Factor-cleaving protease whose loss-of-function causes microvascular thrombosis, were among the proteins most strongly associated with myocardial stress and injury. Findings were validated in a larger COVID-19 patient cohort and the hamster COVID-19 model, providing new insights into the pathophysiology of COVID-19 cardiovascular complications with therapeutic implications.
Keywords: ADAMTS13, A Disintegrin And Metalloproteinase with a Thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13; COVID-19; FSTL3, follistatin-like 3; NT-proBNP, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide; SASP, senescence associated secretory phenotype; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta; hsTnT, high sensitivity troponin T; myocardial injury; proteomics; senescence.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01AG061034 and R35HL15531 [to Dr Rosenzweig]; R01HL092577, R01HL128914, and K24HL105780 [to Dr Ellinor]; R01HL134893, R01HL140224, K24HL153669 [to Dr Ho]; T32HL094301 [to Dr Weber]; K08HL140200 [to Dr Rhee]; and K76AG064328 [to Dr Roh]), the Fondation Leducq (14CVD01 [to Dr Ellinor]), the American Heart Association (18SFRN34110082 [to Dr Ellinor]), a Sarnoff Cardiovascular Research Foundation Fellowship award (to Dr Trager), the Fred and Ines Yeatts Fund for Innovative Research (to Dr Roh), the Hassenfeld Scholars Award (to Dr Roh), Fast Grants, Emergent Ventures, Mercatus Center at George Mason University (to Dr Martinot), and a research grant from Bayer AG to the Broad Institute (to Drs Ellinor and Ho). Dr Ellinor is supported by a grant from Bayer AG to the Broad Institute focused on the genetics and therapeutics of cardiovascular diseases; and has served on advisory boards or consulted for Bayer AG, Quest Diagnostics, MyoKardia and Novartis. Dr Ho has received research grants from Bayer AG and Gilead Sciences; and has received research supplies from EcoNugenics. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures


Update of
-
Plasma Proteomics of COVID-19 Associated Cardiovascular Complications: Implications for Pathophysiology and Therapeutics.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2021 Jun 8:rs.3.rs-539712. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-539712/v1. Res Sq. 2021. Update in: JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2022 May;7(5):425-441. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.01.013. PMID: 34127963 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Comment in
-
Proteomic Analyses Unveil Actionable Disease Pathways in COVID-19: A Step Toward Targeted Therapies.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2022 May 23;7(5):442-444. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.03.011. eCollection 2022 May. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2022. PMID: 35663631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

