Extracellular Vesicles and the Inflammasome: An Intricate Network Sustaining Chemoresistance
- PMID: 35530309
- PMCID: PMC9072732
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.888135
Extracellular Vesicles and the Inflammasome: An Intricate Network Sustaining Chemoresistance
Abstract
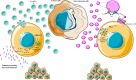
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are membrane enclosed spherical particles devoted to intercellular communication. Cancer-derived EVs (Ca-EVs) are deeply involved in tumor microenvironment remodeling, modifying the inflammatory phenotype of cancerous and non-cancerous residing cells. Inflammation plays a pivotal role in initiation, development, and progression of many types of malignancies. The key feature of cancer-related inflammation is the production of cytokines that incessantly modify of the surrounding environment. Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) is one of the most powerful cytokines, influencing all the initiation-to-progression stages of many types of cancers and represents an emerging critical contributor to chemoresistance. IL-1β production strictly depends on the activation of inflammasome, a cytoplasmic molecular platform sensing exogenous and endogenous danger signals. It has been recently shown that Ca-EVs can activate the inflammasome cascade and IL-1β production in tumor microenvironment-residing cells. Since inflammasome dysregulation has been established as crucial regulator in inflammation-associated tumorigenesis and chemoresistance, it is conceivable that the use of inflammasome-inhibiting drugs may be employed as adjuvant chemotherapy to counteract chemoresistance. This review focuses on the role of cancer-derived EVs in tuning tumor microenvironment unveiling the intricate network between inflammasome and chemoresistance.
Keywords: IL-1β; chemoresistance; extracellular vesicles; inflammasome; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Mezzasoma, Bellezza, Romani and Talesa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EV-Mediated Chemoresistance in the Tumor Microenvironment: Is NF-κB a Player?Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 22;12:933922. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.933922. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35814425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natriuretic Peptides Regulate Prostate Cells Inflammatory Behavior: Potential Novel Anticancer Agents for Prostate Cancer.Biomolecules. 2021 May 25;11(6):794. doi: 10.3390/biom11060794. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34070682 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles from Human Advanced-Stage Prostate Cancer Cells Modify the Inflammatory Response of Microenvironment-Residing Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 30;11(9):1276. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091276. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31480312 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of Endothelial Extracellular Vesicle-Induced Smooth Muscle Phenotype Transition by Hypercholesterolemia Stimulation: Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 21;8:597423. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.597423. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33409276 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Dec 3;9:1342. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01342. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31850225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-derived vesicles in immune modulation: focus on signaling pathways.Front Immunol. 2025 May 15;16:1581964. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1581964. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40443670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EV-Mediated Chemoresistance in the Tumor Microenvironment: Is NF-κB a Player?Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 22;12:933922. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.933922. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35814425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Multifaceted Roles of Extracellular Vesicles: Insights into Biology, Pharmacology, and Pharmaceutical Applications for Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):485. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010485. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lopatina T, Favaro E, Danilova L, Fertig EJ, Favorov AV, Kagohara LT, et al. . Extracellular Vesicles Released by Tumor Endothelial Cells Spread Immunosuppressive and Transforming Signals Through Various Recipient Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol (2020) 8:698. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00698 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lopatina T, Grange C, Cavallari C, Navarro-Tableros V, Lombardo G, Rosso A, et al. . Targeting IL-3Rα on Tumor-Derived Endothelial Cells Blunts Metastatic Spread of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via Extracellular Vesicle Reprogramming. Oncogenesis (2020) 10:90. doi: 10.1038/s41389-020-00274-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

