Development of Diagnosis Model for Early Lung Nodules Based on a Seven Autoantibodies Panel and Imaging Features
- PMID: 35530343
- PMCID: PMC9069812
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.883543
Development of Diagnosis Model for Early Lung Nodules Based on a Seven Autoantibodies Panel and Imaging Features
Abstract
Background: There is increasing incidence of pulmonary nodules due to the promotion and popularization of low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening for potential populations with suspected lung cancer. However, a high rate of false-positive and concern of radiation-related cancer risk of repeated CT scanning remains a major obstacle to its wide application. Here, we aimed to investigate the clinical value of a non-invasive and simple test, named the seven autoantibodies (7-AABs) assay (P53, PGP9.5, SOX2, GAGE7, GUB4-5, MAGEA1, and CAGE), in distinguishing malignant pulmonary diseases from benign ones in routine clinical practice, and construct a neural network diagnostic model with the development of machine learning methods.
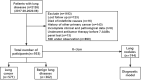
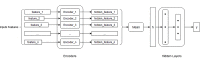
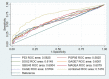
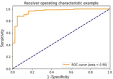
Method: A total of 933 patients with lung diseases and 744 with lung nodules were identified. The serum levels of the 7-AABs were tested by an enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The primary goal was to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the 7-AABs panel in the detection of lung cancer. ROC curves were used to estimate the diagnosis potential of the 7-AABs in different groups. Next, we constructed a machine learning model based on the 7-AABs and imaging features to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy in lung nodules.
Results: The serum levels of all 7-AABs in the malignant lung diseases group were significantly higher than that in the benign group. The sensitivity and specificity of the 7-AABs panel test were 60.7% and 81.5% in the whole group, and 59.7% and 81.1% in cases with early lung nodules. Comparing to the 7-AABs panel test alone, the neural network model improved the AUC from 0.748 to 0.96 in patients with pulmonary nodules.
Conclusion: The 7-AABs panel may be a promising method for early detection of lung cancer, and we constructed a new diagnostic model with better efficiency to distinguish malignant lung nodules from benign nodules which could be used in clinical practice.
Keywords: autoantibodies; early diagnosis; lung cancer; neural network; radiology.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Chang, Yang, Lang, Zhang, Che, Xi, Zhang, Song, Zhou, Yang, Yang, Qu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
QS is employed by Amoy Diagnostics Co. Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

