Comparison of Deep Inspiration Breath Hold Versus Free Breathing in Radiotherapy for Left Sided Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35530354
- PMCID: PMC9069140
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.845037
Comparison of Deep Inspiration Breath Hold Versus Free Breathing in Radiotherapy for Left Sided Breast Cancer
Abstract
Objectives: Modern breast cancer techniques, such as the deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) technique has been applied for left-sided breast cancer. Whether the DIBH regimen is the optimal solution for left-sided breast cancer remains unclear. This meta-analysis aims to elucidate the differences of DIBH and free-breathing (FB) for patients receiving radiotherapy for left-sided breast cancer and provide a practical reference for clinical practice.
Methods: Relevant research available on PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and the Web of Science published before November 30, 2021 was independently and systematically examined by two investigators. Data were extracted from eligible studies for assessing their qualities and calculating the standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using Review Manager software 5.4 (RevMan 5.4).
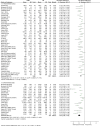
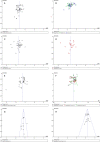
Results: Forty-one studies with a total of 3599 left-sided breast cancer patients were included in the meta-analysis. Compared with FB, DIBH reduced heart dose (D mean, D max, V30, V10, V5), left anterior descending branch (LAD) dose (D mean, D max), ipsilateral lung dose (D mean, V20, V10, V5), and heart volume significantly. Lung volume increased greatly, and a statistically significant difference. For contralateral breast mean dose, DIBH has no obvious advantage over FB. The funnel plot suggested this study has no significant publication bias.
Conclusions: Although DIBH has no obvious advantage over FB in contralateral breast mean dose, it can significantly reduce heart dose, LAD dose, ipsilateral lung dose, and heart volume. Conversely, it can remarkably increase the ipsilateral lung volume. This study suggests that soon DIBH could be more widely utilized in clinical practice because of its excellent dosimetric performance.
Keywords: deep inspiration breath hold; free breathing; left sided breast cancer; meta-analysis; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Yang, Zhang, Teng, Yuan, Zhang, He, Tang, Pang, Han, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, et al. Effects of Radiotherapy and of Differences in the Extent of Surgery for Early Breast Cancer on Local Recurrence and 15-Year Survival: An Overview of the Randomised Trials. Lancet (2005) 366(9503):2087–106. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(05)67887-7 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

