Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Colorectal Cancer With Situs Inversus Totalis by Next-Generation Sequencing
- PMID: 35530355
- PMCID: PMC9067615
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.813253
Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Colorectal Cancer With Situs Inversus Totalis by Next-Generation Sequencing
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most prevalent malignances worldwide. However, CRC with situs inversus totalis (SCRC) is extremely rare, and molecular characterization of this disease has never been investigated.
Methods: Tumor tissue samples from 8 patients with SCRC and 33 CRC patients without situs inversus totalis (NSCRC) were subjected to multigene next-generation sequencing.
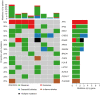
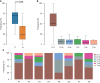
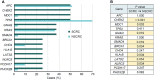
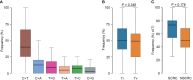
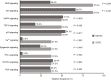
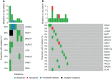
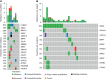
Results: The most frequently mutated genes in SCRC were APC, TP53, CHEK2, MDC1, GNAQ, KRAS, and SMAD4. A high frequency of SCRC tumors had mutations in DNA damage repair genes. Single amino acid substitutions in the DNA damage repair genes caused by continuous double base substitution was identified in the majority of this population. Furthermore, mutational profiles showed notable differences between the SCRC and NSCRC groups. In particular, CHEK2, MDC1, GNAQ, SMAD4, BRCA1, HLA-B, LATS2, and NLRC5 mutations were more frequently observed in SCRC patients. The mutation loci distributions of KRAS in the SCRC cohort differed from that of the NSCRC cohort. Additionally, differences in the targeted genomic profiles and base substitution patterns were observed between the two groups.
Conclusions: These findings comprehensively revealed a molecular characterization of SCRC, which will contribute to the development of personalized therapy and improved clinical management of SCRC patients.
Keywords: NSCRC; SCRC; colorectal cancer; mutational profile; next-generation sequencing.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Gong, Cheng, Wang, Zhang, Rao, Song, Wang, Lou, Lou, Cao, Pan and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
HW, FL, and SC are employees of Acornmed Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of the prognostic value of stromal tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and CD3 + T cells between schistosomal and non-schistosomal colorectal cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Feb 1;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-02911-3. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36726115 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic signatures in young and old Chinese patients with colorectal cancer.Cancer Med. 2021 Jul;10(13):4375-4386. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3987. Epub 2021 May 26. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34041865 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic heterogeneity in synchronous colorectal cancers impacts genotyping approaches and therapeutic strategies.Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2016 Mar;55(3):268-77. doi: 10.1002/gcc.22330. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26650777
-
Renal cell carcinoma with situs inversus totalis.Urology. 1993 May;41(5):455-7. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(93)90507-7. Urology. 1993. PMID: 8488614 Review.
-
Neonatal intestinal obstruction associated with situs inversus totalis: two case reports and a review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Sep 18;11(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1423-z. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28918753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

