Stimulus-induced Robust Narrow-band Gamma Oscillations in Human EEG Using Cartesian Gratings
- PMID: 35530517
- PMCID: PMC9018439
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4379
Stimulus-induced Robust Narrow-band Gamma Oscillations in Human EEG Using Cartesian Gratings
Abstract
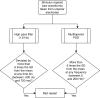
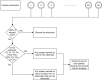
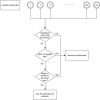
Stimulus-induced narrow-band gamma oscillations (20-70 Hz) are induced in the visual areas of the brain when particular visual stimuli, such as bars, gratings, or full-screen hue, are shown to the subject. Such oscillations are modulated by higher cognitive functions, like attention, and working memory, and have been shown to be abnormal in certain neuropsychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, autism, and Alzheimer's disease. However, although electroencephalogram (EEG) remains one of the most non-invasive, inexpensive, and accessible methods to record brain signals, some studies have failed to observe discernable gamma oscillations in human EEG. In this manuscript, we have described in detail a protocol to elicit robust gamma oscillations in human EEG. We believe that our protocol could help in developing non-invasive gamma-based biomarkers in human EEG, for the early detection of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Artifact rejection; EEG; Gamma; Stimulus-induced gamma.
Copyright © The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Colgin L. L.,Denninger T.,Fyhn M.,Hafting T.,Bonnevie T.,Jensen O.,Moser M. B. and Moser E. I.(2009).Frequency of gamma oscillations routes flow of information in the hippocampus.Nature 462(7271):353-357. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

