Incidence and predictors of mortality among COVID-19 patients admitted to treatment centers in North West Ethiopia; A retrospective cohort study, 2021
- PMID: 35530744
- PMCID: PMC9055687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijans.2022.100419
Incidence and predictors of mortality among COVID-19 patients admitted to treatment centers in North West Ethiopia; A retrospective cohort study, 2021
Abstract
Background: Currently, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is the leading cause of death and the rate of mortality is rapidly increasing over time. There is a paucity of information regarding the incidence and predictors of mortality among COVID-19 patients from low-income countries, particularly in Ethiopia.
Objective: To assess incidence and predictors of mortality among COVID-19 patients admitted to treatment centers in North West Ethiopia.
Methods: An institution-based retrospective cohort study was conducted among 552 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases at Debre Markos University and Tibebe Ghion Hospital COVID-19 treatment centers in North West Ethiopia from March 2020 to March 2021. Data were collected from patients' medical records using a structured data extraction tool. Cox-proportional hazards regression models was fitted to identify significant predictors of mortality.
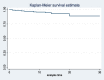
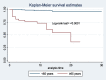
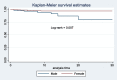
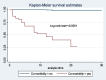
Result: The overall mortality rate of COVID-19 was 4.7, (95 % CI: 3.3-6.8) per 1000 person day observations. Older age (AHR: 4.9; 95% CI: 1.8, 13.5), rural residence (AHR: 0.18; 95% CI: 0.05, 0.64), presence of hypertension (AHR: 3.04; 95% CI: 1.18, 7.8), presence of diabetes mellitus (AHR: 8.1; 95% CI: 2.9, 22.4) and cardiovascular disease (AHR: 5.2; 95% CI: (1.69, 16.2) were significantly associated with mortality.
Conclusions: The rate of mortality among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in this study was low. COVID-19 patients from urban residences, older patients, and patients with comorbidity have a high risk of death. These high risk groups should be prioritized for COVID-19 vaccinations, and early screening and appropriate intervention should be established on presentation to health facility.
Keywords: COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 2019; Coronavirus; DMU, Debre Markos University; Ethiopia; ICU, Intensive Care Unit; Mortality; RT-PCR, Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2; Survival analysis; TGH, Tibebe Ghion Hospital WHO: World Health Organization.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
