A Rare Case of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma With Incidental Synchronous Hepatic and Sigmoid Colonic Metastasis: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 35530817
- PMCID: PMC9076052
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.23921
A Rare Case of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma With Incidental Synchronous Hepatic and Sigmoid Colonic Metastasis: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
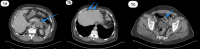
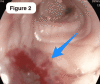
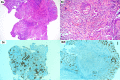
Metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma to the colon is a very rare condition that might be underdiagnosed and underreported in the literature. We report a very rare case of incidental findings of sigmoid metastasis secondary to pancreatic adenocarcinoma in a 60-year-old Saudi male, who is a non-smoker with a normal medical and surgical history. The patient presented to a primary care clinic with abdominal bloating and vague on/off abdominal pain for almost 1 year as well as unintentional weight loss without lower gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms. After the case was discussed in the multidisciplinary tumor board, the patient was started on systematic palliative chemotherapy. However, after receiving the first cycle, he started to deteriorate rapidly and succumbed to secondary cardiopulmonary arrest. Cases of synchronous metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma to the colon might not be well known or common. However, a high index of suspicion and individualizing the workup tools may need to be used.
Keywords: cancer; liver metastasis; mass; pancreatic adenocarcinoma; sigmoid colon metastasis; tumor.
Copyright © 2022, AlAli et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pancreatic cancer presenting as colonic disease. A rare case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2018;44:4-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2018.01.019. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29454229 Free PMC article.
-
Synchronous primary anorectal melanoma and sigmoid adenocarcinoma: a case report.Int Surg. 2015 May;100(5):814-7. doi: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-14-00243. Int Surg. 2015. PMID: 26011200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A left-sided cystic pancreatic incidentaloma with sigmoid colon adenocarcinoma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2018 Aug 30;12(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s13256-018-1778-9. J Med Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30157943 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual Case of Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma Metastasis to the Abdominal Wall 11 Years Later: Synchronous Presentation with Two Malignant Colon Tumors, Coincidence or Not?Case Rep Surg. 2021 Feb 26;2021:6662275. doi: 10.1155/2021/6662275. eCollection 2021. Case Rep Surg. 2021. PMID: 33728090 Free PMC article.
-
Metachronous metastasis to inguinal lymph nodes from sigmoid colon adenocarcinoma with abdominal wall metastasis: a case report.BMC Cancer. 2019 Feb 27;19(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5386-x. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30813921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Case of Isolated Metastasis to the Pleura in the Setting of Newly Diagnosed Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2025 Mar 7;15(2):90-93. doi: 10.55729/2000-9666.1454. eCollection 2025. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2025. PMID: 40309280 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic pancreatic cancer with multiple metastases confined to the large intestine: a case report and literature review.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb;17(1):75-79. doi: 10.1007/s12328-023-01878-8. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38038857 Review.
References
-
- Pancreatic adenocarcinoma with synchronous colonic metastases. Yewale R, Ramakrishna B, Vijaykumar K, et al. https://journals.lww.com/acgcr/fulltext/2020/01000/pancreatic_adenocarci... ACG Case Rep J. 2020;7:0. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
