Regulating mitochondrial homeostasis and inhibiting inflammatory responses through Celastrol
- PMID: 35530963
- PMCID: PMC9073791
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-7015
Regulating mitochondrial homeostasis and inhibiting inflammatory responses through Celastrol
Abstract
Background: The high morbidity and mortality rate of coronary heart disease poses a serious threat to human health. Atherosclerosis, a chronic inflammation of the blood vessel wall, is a significant pathological process leading to coronary heart disease. Macrophage inflammation plays a crucial role in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis.
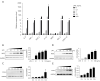
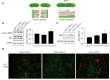
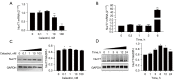
Methods: Macrophage inflammation model was constructed by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and macrophages were treated with Celastrol at different concentrations (0, 0.1, 1, 10, 100 ng/mL) and different time points (0, 1, 3, 6, 12 h). Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) and Western Blot were used to detect the expression of Nur77 mRNA and protein. Macrophages were then pretreated with 100 nmol/L tripterine for 40min and co-cultured with 100 ng/mL LPS. The expression levels of inflammatory factors and chemokines, phosphorylation of phospho-dynamin-related protein 1 (p-Drp1) at Ser637 and expression of mitochondrial fusion protein mitochondrial fusion protein mitofusin-2 (Mfn2) were detected by qPCR, Western blot and ELISA, respectively. The changes of mitochondrial membrane potential were detected by JC-1 probe.
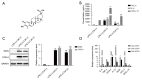
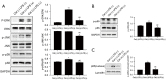
Results: 100 nmol/L Celastrol can significantly inhibit LPS-induced inflammatory responses and down-regulate the expression levels of cytokines such as inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), chemokines (CCL-2, and CXCL-10), as well as chemokines. And Celastrol could regulate mitochondrial fission and fusion by promoting the phosphorylation of the Drp1 at the Ser637 site, thereby inhibiting mitochondrial fission. At the same time, by up-regulating the level of the Mfn2, Celastrol also promoted mitochondrial fusion. In addition, we found that the nuclear factor-k-gene binding (NF-κB), extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and p38 signaling pathways aided the drug's anti-inflammatory effects. We also explored the relationship between Celastrol and the nuclear receptor Nur77 and found that it could up-regulate the expression of Nur77.
Conclusions: Our study found that Celastrol could reduce inflammation by regulating Drp1 dependent mitochondrial fission and fusion, as well as the ERK1/2, p38, NF-κB signaling pathways. This finding provides a strong direction for the development of new anti-inflammatory drugs for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Celastrol; Nur77; dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1); inflammation; mitochondrial fission and fusion.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-21-7015/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
