A combination of the APACHE II score, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, and expired tidal volume could predict non-invasive ventilation failure in pneumonia-induced mild to moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome patients
- PMID: 35530968
- PMCID: PMC9073780
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-22-536
A combination of the APACHE II score, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, and expired tidal volume could predict non-invasive ventilation failure in pneumonia-induced mild to moderate acute respiratory distress syndrome patients
Abstract
Background: Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) failure rate is relatively high in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Currently the data regarding prediction of NIV failure of pneumonia-induced mild to ARDS patients were scarce.
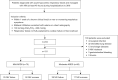
Methods: A total of 364 patients (from January 2016 to December 2020) diagnosed with hypoxemic respiratory failure and managed with NIV were initially included and finally 131 pneumonia-induced mild to moderate ARDS patients were enrolled in this study. Electronic medical records were reviewed to determine whether NIV succeeded or failed for each patient. The relationship between the Acute Physiology And Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score , neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR), expired tidal volume (Vte) and NIV failure were specifically analyzed. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were conducted to identify the independent factors of NIV failure. Receiver-operating characteristic curves were used to assess the efficacy of the variables in predicting NIV failure. Kaplan-Meier curves for 28-day survival were used to compare the mortality rates of different groups.
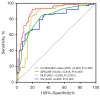
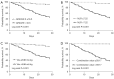
Results: Of the patients, 64 (48.9%) experienced NIV failure, APACHE II score [odds ratio (OR) =0.77; P=0.002], NLR (OR =0.838; P=0.046), and Vte (OR =0.343; P=0.009) were independent factors for predicting NIV failure. A combined value comprising the APACHE II score, NLR, and Vte had better efficacy at predicting NIV failure [area under the curve (AUC) =0.9; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.845-0.955] than the APACHE II score (AUC =0.818; 95% CI: 0.745-0.891), NLR (AUC =0.839; 95% CI: 0.765-0.913), or Vte (AUC =0.805; 95% CI: 0.729-0.881) alone. The cumulative survival probability within 28 days was lower in patients with a combined value >59.17 (P<0.001 by the log-rank test), an APACHE II score >16.5 (P<0.001 by the log-rank test), an NLR >7.22 (P<0.001 by the log-rank test), and a Vte >8.96 mL/kg (P<0.001 by log-rank test).
Conclusions: A combined value comprising an APACHE II score >16.5, a NLR >7.22, and a Vte >8.96 mL/kg may be a useful surrogate for predicting NIV failure among pneumonia-induced ARDS patients, and patients with a combined value >59.17 should be cautiously monitored during NIV. A further study with a larger sample size is warranted.
Keywords: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR); acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS); expired tidal volume (Vte); predictor.
2022 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-536/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Patients with Viral Pneumonia-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: An Observational Retrospective Study.Int J Clin Pract. 2023 Feb 1;2023:1819087. doi: 10.1155/2023/1819087. eCollection 2023. Int J Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 36793926 Free PMC article.
-
[Value of procalcitonin on predicting the severity and prognosis in patients with early ARDS: a prospective observation study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Jan;29(1):34-38. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.01.008. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 28459401 Chinese.
-
[Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on 28-day mortality of patients with severe pneumonia].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019 Jul;31(7):827-831. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.07.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2019. PMID: 31441404 Chinese.
-
[Efficacy of noninvasive ventilation on treatment of ARDS caused by severe pneumonia after kidney transplantation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Nov;29(11):994-998. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.11.007. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 29151414 Chinese.
-
Incidence of noninvasive ventilation failure and mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and proportion meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jan 22;24(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-02839-8. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38254064 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictive value of ELWI combined with sRAGE/esRAGE levels in the prognosis of critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 19;13(1):15463. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42798-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37726414 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of soluble CD40L combined with APACHE II score in elderly patients with sepsis in the emergency department.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Jan 19;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02381-w. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38243164 Free PMC article.
-
[Hypercapnic respiratory failure with insufficient response to fixed-level PS-NIV: Is AVAPS the end solution?].Tuberk Toraks. 2023 Jun;71(2):192-193. doi: 10.5578/tt.20239925. Tuberk Toraks. 2023. PMID: 37345403 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of three common scoring systems in COVID-19 patients: neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), The Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II), and C-reactive protein (CRP).Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Dec 11;86(2):811-818. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001503. eCollection 2024 Feb. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38333304 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
