Nanomedicine: An Emerging Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Hemorrhagic Stroke
- PMID: 35530973
- PMCID: PMC9075782
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S357598
Nanomedicine: An Emerging Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Hemorrhagic Stroke
Abstract
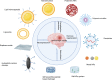
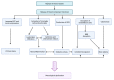
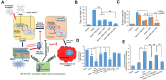
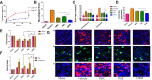
Hemorrhagic stroke is one of the most devastating diseases worldwide due to a high rate of disability and mortality with few effective treatments. Recent advances in nanomedicines to promote hemostasis, drug delivery, neuroprotection, and nerve regeneration may provide insight into hemorrhagic stroke treatment. In this review, we first view the pathophysiology and conventional therapeutics of hemorrhagic stroke. Second, we comprehensively summarize the current nanomedicines applied in hemorrhagic stroke, including inorganic nanomaterials, polymer-based nanomaterials, lipid-based nanomaterials, self-assembling peptide-based hydrogel, exosomes, and gel systems. Finally, the challenges, opportunities, and future perspectives of nanomedicines for hemorrhagic stroke are discussed. Thus, this review promotes greater exploration of effective therapies for hemorrhagic stroke with nanomedicines.
Keywords: hemorrhagic stroke; intracerebral hemorrhage; nanomedicine; subarachnoid hemorrhage; therapy.
© 2022 Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Fernandes HM, et al. Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2005;365(9457):387–397. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)70233-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

