Biomedical Applications of Quantum Dots: Overview, Challenges, and Clinical Potential
- PMID: 35530976
- PMCID: PMC9076002
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S357980
Biomedical Applications of Quantum Dots: Overview, Challenges, and Clinical Potential
Abstract
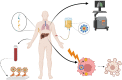
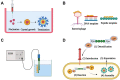
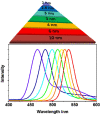
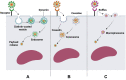
Despite the massive advancements in the nanomedicines and their associated research, their translation into clinically-applicable products is still below promises. The latter fact necessitates an in-depth evaluation of the current nanomedicines from a clinical perspective to cope with the challenges hampering their clinical potential. Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductors-based nanomaterials with numerous biomedical applications such as drug delivery, live imaging, and medical diagnosis, in addition to other applications beyond medicine such as in solar cells. Nevertheless, the power of QDs is still underestimated in clinics. In the current article, we review the status of QDs in literature, their preparation, characterization, and biomedical applications. In addition, the market status and the ongoing clinical trials recruiting QDs are highlighted, with a special focus on the challenges limiting the clinical translation of QDs. Moreover, QDs are technically compared to other commercially-available substitutes. Eventually, we inspire the technical aspects that should be considered to improve the clinical fate of QDs.
Keywords: biosensors; clinical translation; clinical trials; in vivo imaging; photodynamic therapy; quantum dots.
© 2022 Abdellatif et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interests associated with this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

