Molecular docking, pharmacophore based virtual screening and molecular dynamics studies towards the identification of potential leads for the management of H. pylori
- PMID: 35531003
- PMCID: PMC9070323
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03281a
Molecular docking, pharmacophore based virtual screening and molecular dynamics studies towards the identification of potential leads for the management of H. pylori
Abstract
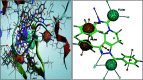
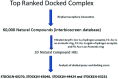
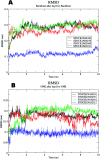
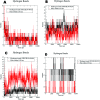
The enzyme pantothenate synthetase panC is one of the potential new antimicrobial drug targets, but it is poorly characterized in H. pylori. H. pylori infection can cause gastric cancer and the management of H. pylori infection is crucial in various gastric ulcers and gastric cancer. The current study describes the use of innovative drug discovery and design approaches like comparative metabolic pathway analysis (Metacyc), exploration of database of essential genes (DEG), homology modelling, pharmacophore based virtual screening, ADMET studies and molecular dynamics simulations in identifying potential lead compounds for the H. pylori specific panC. The top ranked virtual hits STOCK1N-60270, STOCK1N-63040, STOCK1N-44424 and STOCK1N-63231 can act as templates for synthesis of new H. pylori inhibitors and they hold a promise in the management of gastric cancers caused by H. pylori.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures









References
-
- Cancer (Fact sheet N 297), World Health Organization, February 2014, retrieved 2009-05-11, http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
-
- Yamaoka Y., Helicobacter pylori: molecular genetics and cellular biology, Horizon Scientific Press, 2008
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

