Identification and Characterization of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA that Regulates Osteogenesis in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice
- PMID: 35531098
- PMCID: PMC9068931
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.832460
Identification and Characterization of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA that Regulates Osteogenesis in Diet-Induced Obesity Mice
Abstract
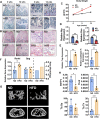
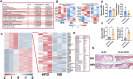
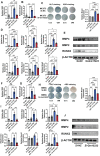
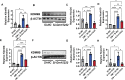
As a precursor to type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D), obesity adversely alters bone cell functions, causing decreased bone quality. Currently, the mechanisms leading to alterations in bone quality in obesity and subsequently T2D are largely unclear. Emerging evidence suggests that long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) participate in a vast repertoire of biological processes and play essential roles in gene expression and posttranscriptional processes. Mechanistically, the expression of lncRNAs is implicated in pathogenesis surrounding the aggregation or alleviation of human diseases. To investigate the functional link between specific lncRNA and obesity-associated poor bone quality and elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between the two, we first assessed the structure of the bones in a diet-induced obese (DIO) mouse model. We found that bone microarchitecture markedly deteriorated in the DIO mice, mainly because of aberrant remodeling in the bone structure. The results of in vitro mechanistic experiments supported these observations. We then screened mRNAs and lncRNAs from DIO bones and functionally identified a specific lncRNA, Gm15222. Further analyses demonstrated that Gm15222 promotes osteogenesis and inhibits the expression of adipogenesis-related genes in DIO via recruitment of lysine demethylases KDM6B and KDM4B, respectively. Through this epigenetic pathway, Gm15222 modulates histone methylation of osteogenic genes. In addition, Gm15222 showed a positive correlation with the expression of a neighboring gene, BMP4. Together, the results of this study identified and provided initial characterization of Gm15222 as a critical epigenetic modifier that regulates osteogenesis and has potential roles in targeting the pathophysiology of bone disease in obesity and potential T2D.
Keywords: BMP4; LncR-DBD; diabetic bone diseases; diet-induced obese; epigenetics; long noncoding RNAs.
Copyright © 2022 Hu, Qiu, Yu, Wu, Fang, Zhu, Xu, Tu, Van Dyke, Morgan and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

