Cardiotoxicity monitoring of pyrotinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide in HER2-positive breast cancer: a single-armed clinical trial
- PMID: 35531104
- PMCID: PMC9068533
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-22-161
Cardiotoxicity monitoring of pyrotinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide in HER2-positive breast cancer: a single-armed clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) inhibitors play a vital role in the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Numerous studies have shown that traditional HER2 inhibitors and chemotherapeutics such as albumin-paclitaxel, liposomal doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TAC regimen) have different degrees of cardiotoxicity. Pyrotinib is a novel small-molecule HER2 inhibitor and has no cardiotoxicity. Here, the purpose of this study was to investigate the cardiac safety of pyrotinib with TAC regimen for HER2-positive breast cancer.
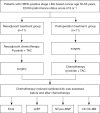
Methods: In this study, 22 patients with stage I-IIIA HER2-positive breast cancer were screened, enrolled, and assigned to receive either neoadjuvant or postoperative adjuvant treatment with pyrotinib (320-400 mg, once daily) combined with TAC (albumin-paclitaxel 260 mg/m2, liposomal doxorubicin 20 mg/m2, cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m2) from December 2019 to May 2021. Patients' heart function was monitored using electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, and serological indicators. ST segment and T wave change, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF, %), N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-pro-BNP), creatine kinase (CK), creatine kinase myoglobin band (CK-MB), together with patients' weight, white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), platelets, plasma lipid, and glucose were recorded.
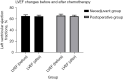
Results: Before and after the 2nd, 4th, and 6th cycles of treatment, the incidence of abnormal electrocardiogram of patients enrolled in the neoadjuvant treatment group was 36.4%, 27.3%, 27.3%, and 27.3%, respectively, while in the postoperative adjuvant treatment, the incidence was 45.5%, 36.4%, 36.4%, and 36.4%, respectively. LVEF before and after treatment in the neoadjuvant chemotherapy group was 65.36%±2.25% and 65.00%±2.15% (t=1.305, P=0.221), while in the postoperative adjuvant treatment group, LVEF was 66.27%±2.69% and 65.18%±1.89% (t=1.359, P=0.204). Pyrotinib combined with a TAC regimen may have induced a decrease in RBC. No obvious abnormality was found in the level of NT-pro-BNP, CK, CK-MB, patients' weight, WBC, platelets, plasma lipid, or glucose in all enrolled patients during the entire treatment process.
Conclusions: Our findings indicated that neither neoadjuvant nor postoperative adjuvant treatment using pyrotinib combined with a TAC regimen to treat patients with HER2-positive breast cancer increased cardiotoxicity. However, the treatment may have induced a decrease in RBC and further research is needed.
Keywords: Cardiotoxicity; HER2-positive breast cancer; chemotherapy; pyrotinib.
2022 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-22-161/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neoadjuvant pyrotinib plus nab-paclitaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide for HER2-positive locally advanced breast cancer: a retrospective case-series study.Gland Surg. 2021 Dec;10(12):3362-3368. doi: 10.21037/gs-21-770. Gland Surg. 2021. PMID: 35070896 Free PMC article.
-
Rationale and design of a phase II trial of pyrotinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel as adjuvant therapy for N0/N1mi, HER2 + early breast cancer (PHAEDRA).BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 14;22(1):269. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09346-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35287613 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Safety of Dual Anti-HER2 Therapy in the Neoadjuvant Setting for Treatment of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Oncologist. 2017 Jun;22(6):642-647. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0406. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28341761 Free PMC article.
-
Docetaxel in the treatment of breast cancer: an update on recent studies.Semin Oncol. 2002 Jun;29(3 Suppl 12):28-34. doi: 10.1053/sonc.2002.34262. Semin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12170449 Review.
-
How to Manage and Monitor Cardiac Dysfunction in Patients With Metastatic HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.JACC CardioOncol. 2022 Sep 20;4(3):404-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2022.06.002. eCollection 2022 Sep. JACC CardioOncol. 2022. PMID: 36213363 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The efficacy and safety of using pyrotinib combined with capecitabine as neoadjuvant therapy in elderly patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: a single-arm prospective clinical trial.Gland Surg. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):208-214. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-11. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 36915823 Free PMC article.
-
Electrocardiographic characteristics of bladder cancer patients receiving preoperative chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2024 Jan;29(1):e13107. doi: 10.1111/anec.13107. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2024. PMID: 38288514 Free PMC article.
-
An exploration of the optimal combination chemotherapy regimen based on neoadjuvant therapy containing pyrotinib for HER2-positive breast cancer: A multicenter real-world study.Transl Oncol. 2025 Jan;51:102173. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2024.102173. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Transl Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39504711 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
