Association of saponin concentration, molecular markers, and biochemical factors with enhancing resistance to alfalfa seedling damping-off
- PMID: 35531163
- PMCID: PMC9072927
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.11.046
Association of saponin concentration, molecular markers, and biochemical factors with enhancing resistance to alfalfa seedling damping-off
Abstract
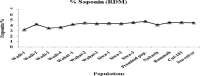
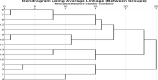
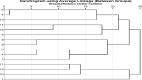
Fifteen alfalfa populations were tested for resistance to the seedling damping-off disease sourced by Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium solani, and Macrophomina phaseolina. In a laboratory experiment, saponin treatment significantly diminished the mycelial growth of the causal fungi of alfalfa damping-off disease. Roots of the fifteen alfalfa populations varied in saponin and lignin content. Selection for the considerably resistant plants leads to the best growth performance, desirable yield, and high nutritive values such as crude protein (CP), crude fier (CF), nitrogen free extract (NFE), ash, and ether extract (EE) contents. For the PCR reaction, 10 SSR pairs of the JESPR series primers and the cDNA-SCoT technique with seven primers were used. SSR and SCoT revealed some unique markers that could be linked to resistance to damping-off disease in alfalfa that appeared in the considerably resistant alfalfa population (the promised pop.). SSR and SCoT markers can be an excellent molecular method for judging genetic diversity and germplasm classification in tetraploid alfalfa. We recommend breeding for saponin concentration in the alfalfa plant may affect resistance to some diseases like root rot and damping-off because saponin might improve plant growth, yield, and nutritional values.
Keywords: Medicago sativa L; Root rot diseases; SCoT Molecular genetic markers; SSR; Saponin and lignin content.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assessment of seed treatments for management of pathogens causing seed rot, seedling damping-off, and seedling root rot in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.).Plant Dis. 2025 Apr 8. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-05-24-1147-RE. Online ahead of print. Plant Dis. 2025. PMID: 40198321
-
Seed Rot and Damping-off of Alfalfa in Minnesota Caused by Pythium and Fusarium Species.Plant Dis. 2017 Nov;101(11):1860-1867. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-02-17-0185-RE. Epub 2017 Aug 28. Plant Dis. 2017. PMID: 30677318
-
Improvement of Biocontrol of Damping-off and Root Rot/Wilt of Faba Bean by Salicylic Acid and Hydrogen Peroxide.Mycobiology. 2013 Mar;41(1):47-55. doi: 10.5941/MYCO.2013.41.1.47. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Mycobiology. 2013. PMID: 23610539 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Diversity and Population Structure of a Worldwide Collection of Cultivated Tetraploid Alfalfa (Medicago sativa subsp. sativa L.) Germplasm as Revealed by Microsatellite Markers.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 22;10(4):e0124592. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124592. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25901573 Free PMC article.
-
Reaction of selected soybean cultivars to Rhizoctonia root rot and other damping-off disease agents.Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2005;70(3):381-90. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16637203
Cited by
-
Simple Sequence Repeat-Based Genetic Diversity Analysis of Alfalfa Varieties.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5246. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115246. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508055 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of potassium nanoparticles as a foliar fertilizer on onion growth, production, chemical content, and DNA fingerprint.Heliyon. 2024 May 22;10(11):e31635. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31635. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38832265 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Genetic Diversity in Alfalfa Using DNA Polymorphism Analysis and Statistical Tools.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;13(20):2853. doi: 10.3390/plants13202853. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdein M.A., Abd El-Moneim D., Taha S.S., Al-Juhani W.S.M., Mohamed S.E. Molecular characterization and genetic relationships among some tomato genotypes as revealed by ISSR and SCoT markers. Egypt. J. Genet. Cytol. 2018;47:139–159.
-
- Abd El-Naby, Zeinab M., Mohamed N., Shaban A., Kh A. Estimation of soil fertility and yield productivity of 3 alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars under Sahl El- Tina saline soils conditions. Life Sci. J. 2013;10(1):2082–2095.
-
- Abd El-Naby Z.M., Azzam C.R., El-Rahman A., Saieda S. Evaluation of ten alfalfa populations for forage yield, protein content, susceptibility to seedling damping-off disease and associated biochemical markers with levels of resistance. J. Am. Sci. 2014;10(7):73–85.
-
- Abdel-Rahman S.S., Omar S.A., Ali A.A.M. Differentiation among Sclerotium rolfesii isolates in response to saponin treatment. Plant Pathol. Quarantine. 2018;8(1):100–109.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

