Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Combined With Bio-Organic Fertilizer Affects the Soil Microbial Community and Yield and Quality of Lettuce
- PMID: 35531292
- PMCID: PMC9069001
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.863325
Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Combined With Bio-Organic Fertilizer Affects the Soil Microbial Community and Yield and Quality of Lettuce
Abstract
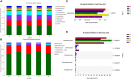
Reducing chemical fertilizers in combination with bio-organic fertilizers can limit the use of chemical fertilizers while maintaining soil fertility. However, the effects of combined fertilization on soil chemical properties, microbial community structure, and crop yield and quality are unknown. Using high-throughput sequencing, we conducted field experiments using lettuce plants subjected to five fertilization treatments: chemical fertilizer with conventional fertilization rate (CK), chemical fertilizer reduction by 30% + 6,000 kg ha-1 bio-organic fertilizer (T1), chemical fertilizer reduction by 30% + 9,000 kg ha-1 bio-organic fertilizer (T2), chemical fertilizer reduction by 40% + 6,000 kg ha-1 bio-organic fertilizer (T3), and chemical fertilizer reduction by 40% + 9,000 kg ha-1 bio-organic fertilizer (T4). Compared with CK, the T1-T4 had significantly higher soil pH and soil organic matter (SOM) and showed increased richness and diversity of the bacterial community, and decreased richness and diversity of the fungal community. Principal coordinate analysis evidenced that the bacterial and fungal communities of CK and T1-T4 were distinctly separated. The Kruskal-Wallis H-test demonstrated that the fungal community was more sensitive than the bacterial community to chemical fertilizer reduction combined with bio-organic fertilizer. Among the soil chemical parameters measured, only TN (total nitrogen) was significantly correlated with bacterial and fungal community composition. The T1 and T2 increased lettuce yield. Moreover, T1-T4 characterized reduced nitrate content and increased levels of soluble sugars and vitamin C in lettuce. Overall, the combined application of reduced chemical fertilizer and bio-organic fertilizer effectively improved soil fertility, microbial community structure, and lettuce yield and quality. These findings have valuable implications for vegetable safety and long-term environmental sustainability.
Keywords: bacterial community; bio-organic fertilizer; chemical fertilizer; fungal community; high-throughput sequencing.
Copyright © 2022 Jin, Jin, Wang, Li, Liu, Liu, Luo, Wu, Lyu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Changes in the Microbial Structure of the Root Soil and the Yield of Chinese Baby Cabbage by Chemical Fertilizer Reduction with Bio-Organic Fertilizer Application.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0121522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01215-22. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36377898 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Different Microbial Fertilizers on Soil Quality and Maize Yield in Coastal Saline Soil].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024 Jul 8;45(7):4279-4292. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202307148. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024. PMID: 39022973 Chinese.
-
Effects of nitrogen reduction combined with bio-organic fertilizer on soil bacterial community diversity of red raspberry orchard.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 11;18(7):e0283718. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283718. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37432967 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus Bio-Organic Fertilizer Altered Soil Microorganisms and Improved Yield and Quality of Radish (Raphanus sativus L.).Plants (Basel). 2025 May 5;14(9):1389. doi: 10.3390/plants14091389. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364418 Free PMC article.
-
[Response of Bacterial and Fungal Communities to Chemical Fertilizer Reduction Combined with Organic Fertilizer and Straw in Fluvo-aquic Soil].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020 Oct 8;41(10):4669-4681. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202003068. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020. PMID: 33124400 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and diversity and yield of cotton.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 20;14:1295722. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1295722. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38053554 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the utilization of main crop straw resources in Southern China and its potential as a replacement for chemical fertilizers.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 5;14:1172689. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1172689. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38250439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of long-term different fertilization regimes on microbial utilization of straw-derived carbon in greenhouse vegetable soils: insights from its ecophysiological roles and temperature responses.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Oct 25;15:1486817. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1486817. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39524564 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of the combined application of biochar and organic fertilizer on the growth and nutrient distribution in wheat under reduced chemical fertilizer conditions.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 12;15(1):5285. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88879-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39939682 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and molecular insight of microbial biostimulants for sustainable agriculture.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 30;14:1041413. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1041413. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36794211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afreh D., Zhang J., Guan D., Liu K., Song Z., Zheng C., et al. (2018). Long-term fertilization on nitrogen use efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in a double maize cropping system in subtropical China. Soil Till. Res. 180 259–267. 10.1016/j.still.2018.03.016 - DOI
-
- Ai C., Liang G., Sun J., Wang X., Zhou W. (2012). Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 173 330–338. 10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.07.020 - DOI
-
- Arya S., Mahajan M., Jain P. (2000). Non-spectrophotometric methods for the determination of Vitamin C. Anal. Chim. Acta 417 1–14. 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)00909-0 - DOI
-
- Bandyopadhyay K., Misra A., Ghosh P., Hati K. (2010). Effect of integrated use of farmyard manure and chemical fertilizers on soil physical properties and productivity of soybean. Soil Till. Res. 110 115–125. 10.1016/j.still.2010.07.007 - DOI
-
- Bei S., Zhang Y., Li T., Christie P., Li X., Zhang J. (2018). Response of the soil microbial community to different fertilizer inputs in a wheat-maize rotation on a calcareous soil. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 260 58–69. 10.1016/j.agee.2018.03.014 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

