A Survey on Industrial Internet of Things: A Cyber-Physical Systems Perspective
- PMID: 35531371
- PMCID: PMC9074819
- DOI: 10.1109/access.2018.2884906
A Survey on Industrial Internet of Things: A Cyber-Physical Systems Perspective
Abstract
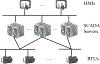
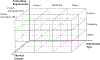
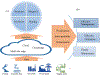
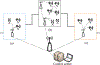
The vision of Industry 4.0, otherwise known as the fourth industrial revolution, is the integration of massively deployed smart computing and network technologies in industrial production and manufacturing settings for the purposes of automation, reliability, and control, implicating the development of an Industrial Internet of Things (I-IoT). Specifically, I-IoT is devoted to adopting the Internet of Things (IoT) to enable the interconnection of anything, anywhere, and at anytime in the manufacturing system context to improve the productivity, efficiency, safety and intelligence. As an emerging technology, I-IoT has distinct properties and requirements that distinguish it from consumer IoT, including the unique types of smart devices incorporated, network technologies and quality of service requirements, and strict needs of command and control. To more clearly understand the complexities of I-IoT and its distinct needs, and to present a unified assessment of the technology from a systems perspective, in this paper we comprehensively survey the body of existing research on I-IoT. Particularly, we first present the I-IoT architecture, I-IoT applications (i.e., factory automation (FA) and process automation (PA)) and their characteristics. We then consider existing research efforts from the three key systems aspects of control, networking and computing. Regarding control, we first categorize industrial control systems and then present recent and relevant research efforts. Next, considering networking, we propose a three-dimensional framework to explore the existing research space, and investigate the adoption of some representative networking technologies, including 5G, machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, and software defined networking (SDN). Similarly, concerning computing, we again propose a second three-dimensional framework that explores the problem space of computing in I-IoT, and investigate the cloud, edge, and hybrid cloud and edge computing platforms. Finally, we outline particular challenges and future research needs in control, networking, and computing systems, as well as for the adoption of machine learning, in an I-IoT context.
Keywords: Application and Service; Big Data Analytics; Computing; Control; Future Research Directions; Industrial Cyber Physical Systems; Industrial Internet of Things; Machine Learning; Networking; Survey.
Figures
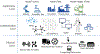

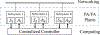
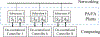

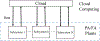



References
-
- Jeong S, Na W, Kim J, and Cho S, “Internet of Things for smart manufacturing system: Trust issues in resource allocation,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018.
-
- Lin J, Yu W, Zhang N, Yang X, Zhang H, and Zhao W, “A survey on Internet of Things: Architecture, enabling technologies, security and privacy, and applications,” IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 1125–1142, 2017.
-
- Lu Y, “Industry 4.0: A survey on technologies, applications and open research issues,” Journal of Industrial Information Integration, vol. 6, pp. 1–10, 2017.
-
- Columbus L, “Roundup of Internet of Things forecasts and market estimates, 2016. forbes, november 27, 2016,” https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2016/11/27/roundup-of-interne..., 2016.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
