MicroRNAs in kidney development and disease
- PMID: 35531954
- PMCID: PMC9090243
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.158277
MicroRNAs in kidney development and disease
Abstract
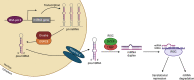
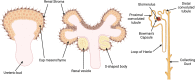
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) belong to a class of endogenous small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the posttranscriptional level, through both translational repression and mRNA destabilization. They are key regulators of kidney morphogenesis, modulating diverse biological processes in different renal cell lineages. Dysregulation of miRNA expression disrupts early kidney development and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of developmental kidney diseases. In this Review, we summarize current knowledge of miRNA biogenesis and function and discuss in detail the role of miRNAs in kidney morphogenesis and developmental kidney diseases, including congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract and Wilms tumor. We conclude by discussing the utility of miRNAs as potentially novel biomarkers and therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

