CRISPR/Cas9 disruption of UGT71L1 in poplar connects salicinoid and salicylic acid metabolism and alters growth and morphology
- PMID: 35532172
- PMCID: PMC9338807
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koac135
CRISPR/Cas9 disruption of UGT71L1 in poplar connects salicinoid and salicylic acid metabolism and alters growth and morphology
Abstract
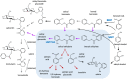
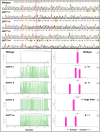
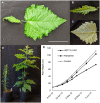
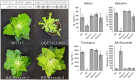
Salicinoids are salicyl alcohol-containing phenolic glycosides with strong antiherbivore effects found only in poplars and willows. Their biosynthesis is poorly understood, but recently a UDP-dependent glycosyltransferase, UGT71L1, was shown to be required for salicinoid biosynthesis in poplar tissue cultures. UGT71L1 specifically glycosylates salicyl benzoate, a proposed salicinoid intermediate. Here, we analyzed transgenic CRISPR/Cas9-generated UGT71L1 knockout plants. Metabolomic analyses revealed substantial reductions in the major salicinoids, confirming the central role of the enzyme in salicinoid biosynthesis. Correspondingly, UGT71L1 knockouts were preferred to wild-type by white-marked tussock moth (Orgyia leucostigma) larvae in bioassays. Greenhouse-grown knockout plants showed substantial growth alterations, with decreased internode length and smaller serrated leaves. Reinserting a functional UGT71L1 gene in a transgenic rescue experiment demonstrated that these effects were due only to the loss of UGT71L1. The knockouts contained elevated salicylate (SA) and jasmonate (JA) concentrations, and also had enhanced expression of SA- and JA-related genes. SA is predicted to be released by UGT71L1 disruption, if salicyl salicylate is a pathway intermediate and UGT71L1 substrate. This idea was supported by showing that salicyl salicylate can be glucosylated by recombinant UGT71L1, providing a potential link of salicinoid metabolism to SA and growth impacts. Connecting this pathway with growth could imply that salicinoids are under additional evolutionary constraints beyond selective pressure by herbivores.
� American Society of Plant Biologists 2022. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



Comment in
-
CRISPR-Cas9 helps solve a piece of the puzzle of the biosynthesis of salicinoids and suggests a role in the growth-defense trade-off in poplar.Plant Cell. 2022 Jul 30;34(8):2819-2820. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koac157. Plant Cell. 2022. PMID: 35640826 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Babst BA, Harding SA, Tsai CJ (2010) Biosynthesis of phenolic glycosides from phenylpropanoid and benzenoid precursors in Populus. J Chem Ecol 36: 286–297 - PubMed
-
- Basey JM, Jenkins SH, Busher PE (1988) Optimal central-place foraging by beavers: tree-size selection in relation to defensive chemicals of quaking aspen. Oecologia 76: 278–282 - PubMed
-
- Brunner AM, Busov VB, Strauss SH (2004) Poplar genome sequence: functional genomics in an ecologically dominant plant species. Trends Plant Sci 9: 49–56 - PubMed
-
- Boeckler G, Gershenzon J, Unsicker S (2011) Phenolic glycosides of the Salicaceae and their role as anti-herbivore defenses. Phytochemistry 72: 1497–1509 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

