Switching off Bacterial Flagellar Biogenesis by YdiU-Mediated UMPylation of FlhDC
- PMID: 35532215
- PMCID: PMC9239255
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00249-22
Switching off Bacterial Flagellar Biogenesis by YdiU-Mediated UMPylation of FlhDC
Abstract
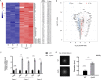
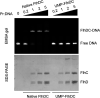
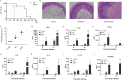
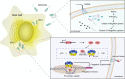
Bacterial flagellin activates the host immune system and triggers pyroptosis. Salmonella reduces flagellin expression when it survives within host cells. Here, we found that the UMPylator YdiU significantly altered the Salmonella flagellar biogenesis process upon host cell entry. The expression levels of class II and class III flagellar genes, but not the class I flagellar genes flhDC, were dramatically increased in a ΔydiU strain compared to wild-type (WT) Salmonella in a host-simulating environment. A direct interaction between YdiU and FlhDC was detected by bacterial two-hybrid assay. Furthermore, YdiU efficiently catalyzed the UMPylation of FlhC but not FlhD, FliA, or FliC. UMPylation of FlhC completely eliminated its DNA-binding activity. In vivo experiments showed that YdiU was required and sufficient for Salmonella flagellar control within host cells. Mice infected with the ΔydiU strain died much earlier than WT strain-infected mice and developed much more severe inflammation and injury in organs and much higher levels of cytokines in blood, demonstrating that early host death induced by the ΔydiU strain is probably due to excessive inflammation. Our results indicate that YdiU acts as an essential factor of Salmonella to mediate host immune escape. IMPORTANCE Salmonella is an important facultative pathogen of foodborne illness and typhoid fever in humans. Flagella allow bacterial motility and are required for Salmonella to successfully invade the host cells. In parallel, flagellin triggers the host immune system. Salmonella reduces flagellar biogenesis to avoid detection within host cells by a largely unknown mechanism. Here, we report that the UMPylator YdiU inhibits flagellin expression in response to host signals in an UMPylation-dependent manner. The target of YdiU is the major flagellar transcription factor FlhDC. YdiU UMPylates the FlhC subunit on its Ser31 residue and prevents FlhDC from binding to flagellar genes, thus switching off flagellar biogenesis. Our results reveal a novel mechanism by which Salmonella adopts posttranslational modification to shut down flagellar synthesis as a strategy to achieve immune escape.
Keywords: FlhDC; Salmonella; UMPylation; YdiU; flagellar gene regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Salmonella Facilitates Iron Acquisition through UMPylation of Ferric Uptake Regulator.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0020722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00207-22. Epub 2022 May 9. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35532216 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative Regulation of Flagellar Synthesis by Two EAL-Like Proteins upon Salmonella Entry into Host Cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 7;11(2):e0285922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02859-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36749049 Free PMC article.
-
Swimming motility, a virulence trait of Ralstonia solanacearum, is regulated by FlhDC and the plant host environment.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004 Jun;17(6):686-95. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2004.17.6.686. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2004. PMID: 15195951
-
[Salmonella multiphasic flagellar antigen].Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012 Jun 26;66:446-51. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1001631. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2012. PMID: 22922144 Review. Polish.
-
Flagella at the Host-Microbe Interface: Key Functions Intersect With Redundant Responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 24;13:828758. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.828758. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35401545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trans-cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsion reduces Salmonella Enteritidis biofilm on steel and plastic surfaces and downregulates expression of biofilm associated genes.Poult Sci. 2025 May;104(5):105086. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105086. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40168703 Free PMC article.
-
A c-di-GMP binding effector STM0435 modulates flagellar motility and pathogenicity in Salmonella.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2331265. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2331265. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38532247 Free PMC article.
-
Host acid signal controls Salmonella flagella biogenesis through CadC-YdiV axis.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2146979. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2146979. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 36456534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horstmann JA, Lunelli M, Cazzola H, Heidemann J, Kuhne C, Steffen P, Szefs S, Rossi C, Lokareddy RK, Wang C, Lemaire L, Hughes KT, Uetrecht C, Schluter H, Grassl GA, Stradal TEB, Rossez Y, Kolbe M, Erhardt M. 2020. Methylation of Salmonella Typhimurium flagella promotes bacterial adhesion and host cell invasion. Nat Commun 11:2013. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15738-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

