Cell-Lineage Guided Mass Spectrometry Proteomics in the Developing (Frog) Embryo
- PMID: 35532271
- PMCID: PMC9513837
- DOI: 10.3791/63586
Cell-Lineage Guided Mass Spectrometry Proteomics in the Developing (Frog) Embryo
Abstract
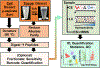
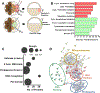
Characterization of molecular events as cells give rise to tissues and organs raises a potential to better understand normal development and design efficient remedies for diseases. Technologies enabling accurate identification and quantification of diverse types and large numbers of proteins would provide still missing information on molecular mechanisms orchestrating tissue and organism development in space and time. Here, we present a mass spectrometry-based protocol that enables the measurement of thousands of proteins in identified cell lineages in Xenopus laevis (frog) embryos. The approach builds on reproducible cell-fate maps and established methods to identify, fluorescently label, track, and sample cells and their progeny (clones) from this model of vertebrate development. After collecting cellular contents using microsampling or isolating cells by dissection or fluorescence-activated cell sorting, proteins are extracted and processed for bottom-up proteomic analysis. Liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis are used to provide scalable separation for protein detection and quantification with high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). Representative examples are provided for the proteomic characterization of neural-tissue fated cells. Cell-lineage-guided HRMS proteomics is adaptable to different tissues and organisms. It is sufficiently sensitive, specific, and quantitative to peer into the spatio-temporal dynamics of the proteome during vertebrate development.
Figures

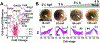
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
