Assessment of Neutralizing Antibody Response Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants After 2 to 3 Doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
- PMID: 35532938
- PMCID: PMC9086840
- DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.10780
Assessment of Neutralizing Antibody Response Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants After 2 to 3 Doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine
Abstract
Importance: Although 2 and 3 doses of vaccine have been implemented against the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the level of immunity achieved by these additional vaccinations remains unclear.
Objective: To investigate the induction of neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant after 2 and 3 doses of the BNT162b2 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine among recipients of different ages.
Design, setting, and participants: A cohort study was conducted from June 1, 2021, to January 12, 2022, among 82 physicians at Kobe University Hospital who had received 2 doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine.
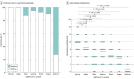
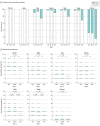
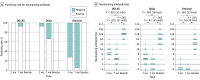
Main outcomes and measures: The rates of positive test results and the titers of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant after 2 and 3 doses of the vaccine were compared with those against other variants and compared among 3 age groups (≤38 years [younger age group], 39-58 years [intermediate age group], and ≥59 years [older age group]).
Results: A total of 82 physicians (71 men [87%]; median age, 44 years [IQR, 33-58 years]) participated; 31 (38%) were in the younger age group, 32 (39%) were in the intermediate age group, and 19 (23%) were in the older age group. At 2 months after 2 doses of the vaccine, 23 participants (28%) had neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant, with a titer of 1.3 (95% CI, 1.2-1.4), which was 11.8-fold (95% CI, 9.9-13.9) lower than the titer against the D614G variant and the lowest among the variants tested. Although the titer of the neutralizing antibody against the Delta variant tended to be low among the older age group (2.9 [95% CI, 2.0-4.1]), the titers of the neutralizing antibody against the Omicron variant were low among all age groups (younger age group, 1.3 [95% CI, 1.1-1.6]; intermediate age group, 1.3 (95% CI, [95% CI, 1.1-1.5]; and older age group, 1.2 [95% CI, 1.0-1.4]). At 7 months after 2 doses of the vaccine, 5 participants (6%) had the neutralizing antibody against the Omicron variant, but after the booster (third dose) vaccination, all 72 participants who received the booster had the neutralizing antibody, and the titer was 41 (95% CI, 34-49), much higher than that at 7 months after 2 doses of the vaccine (1.0 [95% CI, 1.0-1.1]). This increase in titers was observed regardless of age groups; the titers were 44 (95% CI, 32-59) among the younger age group, 44 (95% CI, 32-59) among the intermediate age group, and 30 (95% CI, 22-41) among the older age group.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study of 82 Japanese participants, 2 doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine did not induce sufficient neutralizing antibody against the Omicron variant. However, booster vaccination was associated with induction of a high level of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant, irrespective of the recipient's age.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Durability of Immune Response After COVID-19 Booster Vaccination and Association With COVID-19 Omicron Infection.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Sep 1;5(9):e2231778. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.31778. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36107426 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants following heterologous CoronaVac plus BNT162b2 booster vaccination.Nat Med. 2022 Mar;28(3):481-485. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01705-6. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35051990 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of COVID-19 vaccine responses and third booster dose-induced neutralizing antibodies against Delta and Omicron variants.Nat Commun. 2022 May 5;13(1):2476. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30162-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35513437 Free PMC article.
-
The Vaccine Efficacy Against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 13;10:940956. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940956. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35910897 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical development of variant-adapted BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccines: the early Omicron era.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2023 Jan-Dec;22(1):650-661. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2023.2232851. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2023. PMID: 37417000 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 variants after immunization with different vaccines in Mexico.Epidemiol Infect. 2024 Feb 5;152:e30. doi: 10.1017/S0950268824000219. Epidemiol Infect. 2024. PMID: 38312015 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 variants after 2 doses of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in a correctional facility.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Dec 30;18(7):2153537. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2153537. Epub 2022 Dec 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 36503363 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralizing antibodies and safety of a COVID-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 wild-type and Omicron variants in solid cancer patients.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 7;19(11):e0310781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310781. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39509358 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and laboratory considerations: determining an antibody-based composite correlate of risk for reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 or severe COVID-19.Front Public Health. 2023 Dec 28;11:1290402. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1290402. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38222091 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 vaccine effectiveness against symptomatic infection and hospitalisation in Belgium, July 2021 to May 2022.Euro Surveill. 2023 Jun;28(26):2200768. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2023.28.26.2200768. Euro Surveill. 2023. PMID: 37382885 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

