Comparison Between the 24-hour Holter Test and 72-hour Single-Lead Electrocardiogram Monitoring With an Adhesive Patch-Type Device for Atrial Fibrillation Detection: Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 35532989
- PMCID: PMC9127648
- DOI: 10.2196/37970
Comparison Between the 24-hour Holter Test and 72-hour Single-Lead Electrocardiogram Monitoring With an Adhesive Patch-Type Device for Atrial Fibrillation Detection: Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: There is insufficient evidence for the use of single-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring with an adhesive patch-type device (APD) over an extended period compared to that of the 24-hour Holter test for atrial fibrillation (AF) detection.
Objective: In this paper, we aimed to compare AF detection by the 24-hour Holter test and 72-hour single-lead ECG monitoring using an APD among patients with AF.
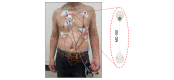
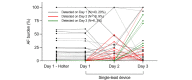
Methods: This was a prospective, single-center cohort study. A total of 210 patients with AF with clinical indications for the Holter test at cardiology outpatient clinics were enrolled in the study. The study participants were equipped with both the Holter device and APD for the first 24 hours. Subsequently, only the APD continued ECG monitoring for an additional 48 hours. AF detection during the first 24 hours was compared between the two devices. The diagnostic benefits of extended monitoring using the APD were evaluated.
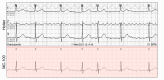
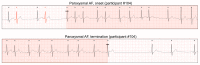
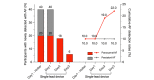
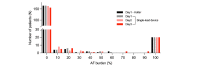
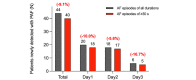
Results: A total of 200 patients (mean age 60 years; n=141, 70.5% male; and n=59, 29.5% female) completed 72-hour ECG monitoring with the APD. During the first 24 hours, both monitoring methods detected AF in the same 40/200 (20%) patients (including 20 patients each with paroxysmal and persistent AF). Compared to the 24-hour Holter test, the APD increased the AF detection rate by 1.5-fold (58/200; 29%) and 1.6-fold (64/200; 32%) with 48- and 72-hour monitoring, respectively. With the APD, the number of newly discovered patients with paroxysmal AF was 20/44 (45.5%), 18/44 (40.9%), and 6/44 (13.6%) at 24-, 48-, and 72-hour monitoring, respectively. Compared with 24-hour Holter monitoring, 72-hour monitoring with the APD increased the detection rate of paroxysmal AF by 2.2-fold (44/20).
Conclusions: Compared to the 24-hour Holter test, AF detection could be improved with 72-hour single-lead ECG monitoring with the APD.
Keywords: ECG; EKG; Holter; arrhythmia; atrial fibrillation; cardiac; cardiac health; cardiology; clinician; diagnosis; diagnostic; digital health; digital tool; electrocardiogram; health monitoring; outpatient clinic; patient; patient monitoring; wearable device.
©Soonil Kwon, So-Ryoung Lee, Eue-Keun Choi, Hyo-Jeong Ahn, Hee-Seok Song, Young-Shin Lee, Seil Oh, Gregory Y H Lip. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 09.05.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: HSH and YSL: stockholders of Seers Technology Co, Ltd. EKC: research grants or speaking fees from Abbott, Bayer, BMS/Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Chong Kun Dang, Daewoong Pharmaceutical Co, Daiichi-Sankyo, DeepQure, Dreamtech Co, Ltd, Jeil Pharmaceutical Co Ltd, Medtronic, Samjinpharm, Seers Technology, and Skylabs. Stock options from Seers Technology, and Skylabs; GYHL: Consultant for Bayer/Janssen, BMS/Pfizer, Medtronic, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Verseon and Daiichi-Sankyo. Speaker for Bayer, BMS/Pfizer, Medtronic, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Daiichi-Sankyo. No fees are received personally. SK, SRL, HJA, and SO have none to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, Boriani G, Castella M, Dan GA, Dilaveris PE, Fauchier L, Filippatos G, Kalman JM, La Meir M, Lane DA, Lebeau JP, Lettino M, Lip GYH, Pinto FJ, Thomas GN, Valgimigli M, Van Gelder IC, Van Putte BP, Watkins CL, ESC Scientific Document Group 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2021 Feb 01;42(5):373–498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612.5899003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shen WK, Sheldon RS, Benditt DG, Cohen MI, Forman DE, Goldberger ZD, Grubb BP, Hamdan MH, Krahn AD, Link MS, Olshansky B, Raj SR, Sandhu RK, Sorajja D, Sun BC, Yancy CW. 2017 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Patients With Syncope: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2017 Aug 01;136(5):e60–e122. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000499.CIR.0000000000000499 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sana F, Isselbacher EM, Singh JP, Heist EK, Pathik B, Armoundas AA. Wearable Devices for Ambulatory Cardiac Monitoring: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Apr 07;75(13):1582–1592. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.01.046. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0735-1097(20)30523-4 S0735-1097(20)30523-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Reynolds K, Yang J, Gupta N, Lenane J, Sung SH, Harrison TN, Liu TI, Solomon MD. Association of Burden of Atrial Fibrillation With Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Adults With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation: The KP-RHYTHM Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2018 Jul 01;3(7):601–608. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2018.1176. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29799942 2681476 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett PM, Komatireddy R, Haaser S, Topol S, Sheard J, Encinas J, Fought AJ, Topol EJ. Comparison of 24-hour Holter monitoring with 14-day novel adhesive patch electrocardiographic monitoring. Am J Med. 2014 Jan;127(1):95.e11–95.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.10.003. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0002-9343(13)00870-X S0002-9343(13)00870-X - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

