Ubiquitination of Ebola virus VP35 at lysine 309 regulates viral transcription and assembly
- PMID: 35533195
- PMCID: PMC9119628
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010532
Ubiquitination of Ebola virus VP35 at lysine 309 regulates viral transcription and assembly
Abstract
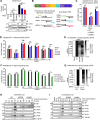
Ebola virus (EBOV) VP35 is a polyfunctional protein involved in viral genome packaging, viral polymerase function, and host immune antagonism. The mechanisms regulating VP35's engagement in different functions are not well-understood. We previously showed that the host E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM6 ubiquitinates VP35 at lysine 309 (K309) to facilitate virus replication. However, how K309 ubiquitination regulates the function of VP35 as the viral polymerase co-factor and the precise stage(s) of the EBOV replication cycle that require VP35 ubiquitination are not known. Here, we generated recombinant EBOVs encoding glycine (G) or arginine (R) mutations at VP35/K309 (rEBOV-VP35/K309G/-R) and show that both mutations prohibit VP35/K309 ubiquitination. The K309R mutant retains dsRNA binding and efficient type-I Interferon (IFN-I) antagonism due to the basic residue conservation. The rEBOV-VP35/K309G mutant loses the ability to efficiently antagonize the IFN-I response, while the rEBOV-VP35/K309R mutant's suppression is enhanced. The replication of both mutants was significantly attenuated in both IFN-competent and -deficient cells due to impaired interactions with the viral polymerase. The lack of ubiquitination on VP35/K309 or TRIM6 deficiency disrupts viral transcription with increasing severity along the transcriptional gradient. This disruption of the transcriptional gradient results in unbalanced viral protein production, including reduced synthesis of the viral transcription factor VP30. In addition, lack of ubiquitination on K309 results in enhanced interactions with the viral nucleoprotein and premature nucleocapsid packaging, leading to dysregulation of virus assembly. Overall, we identified a novel role of VP35 ubiquitination in coordinating viral transcription and assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Host E3-Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM6 Ubiquitinates the Ebola Virus VP35 Protein and Promotes Virus Replication.J Virol. 2017 Aug 24;91(18):e00833-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00833-17. Print 2017 Sep 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28679761 Free PMC article.
-
Ebola Virus Inclusion Body Formation and RNA Synthesis Are Controlled by a Novel Domain of Nucleoprotein Interacting with VP35.J Virol. 2020 Jul 30;94(16):e02100-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02100-19. Print 2020 Jul 30. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32493824 Free PMC article.
-
dsRNA binding characterization of full length recombinant wild type and mutants Zaire ebolavirus VP35.Antiviral Res. 2012 Mar;93(3):354-63. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.01.005. Epub 2012 Jan 25. Antiviral Res. 2012. PMID: 22289166 Free PMC article.
-
Evasion of interferon responses by Ebola and Marburg viruses.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):511-20. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0076. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19694547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Ebola Virus VP35 and VP24 Interferon Inhibitory Functions and their Initial Exploitation as Drug Targets.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019;19(4):362-374. doi: 10.2174/1871526519666181123145540. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2019. PMID: 30468131 Review.
Cited by
-
Ebola virus sequesters IRF3 in viral inclusion bodies to evade host antiviral immunity.Elife. 2024 Jan 29;12:RP88122. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88122. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38285487 Free PMC article.
-
Ebola virus VP35 interacts non-covalently with ubiquitin chains to promote viral replication.PLoS Biol. 2024 Feb 29;22(2):e3002544. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002544. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38422166 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of the Ubiquitin-Mediated Signaling Pathway Exhibit Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activities against New World Alphaviruses.Viruses. 2023 Feb 28;15(3):655. doi: 10.3390/v15030655. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992362 Free PMC article.
-
A No-Brainer! The Therapeutic Potential of TRIM Proteins in Viral and Central Nervous System Diseases.Viruses. 2025 Apr 14;17(4):562. doi: 10.3390/v17040562. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40285004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Fraction Proteome Analyses During rAAV Production of AAV2-Plasmid-Transfected HEK-293 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 30;26(13):6315. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136315. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- CDC. Ebola (Ebola Virus Disease) History of Ebola Outbreaks: CDC; 2021. [updated 2021. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/history/chronology.html#anchor_1526565058132.
-
- Feldmann H, Sprecher A, Geisbert TW. Ebola. The New England journal of medicine. 2020;382(19). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

