Novel Regioselective Synthesis of Urolithin Glucuronides─Human Gut Microbiota Cometabolites of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid
- PMID: 35533350
- PMCID: PMC9121390
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00170
Novel Regioselective Synthesis of Urolithin Glucuronides─Human Gut Microbiota Cometabolites of Ellagitannins and Ellagic Acid
Abstract
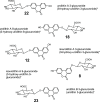
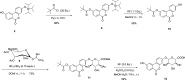
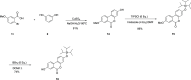
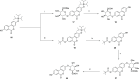
Urolithins (dibenzo-pyran-[b,d]-6 one derivatives) are human gut microbiota metabolites produced from the natural food antioxidant ellagic acid. Urolithins are better absorbed than ellagic acid and demonstrate biological activities that suggest that they are responsible for the health effects observed after consuming ellagitannin- and ellagic acid-containing foods. Urolithins occur in the systemic circulation as glucuronide conjugates following phase II metabolism. These phase II conjugates are essential for testing the urolithin mechanisms of action in human cell line bioassays. Urolithin glucuronides are not commercially available, and their biosynthesis leads to mixtures of regional isomers. This study describes a novel and regioselective synthesis of urolithin A (3,8-dihydroxy urolithin) 3- and 8-glucuronides and isourolithin A (3,9-dihydroxy urolithin) 3- and 9-glucuronides. The metabolites were characterized using 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and UV spectrophotometry. The presence of these metabolites in human subjects belonging to different urolithin metabotypes was also investigated.
Keywords: ellagic acid; glucuronides; gut microbiota metabolites; synthesis; urolithins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

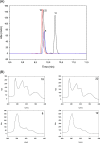
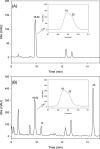
References
-
- Cerdá B.; Espín J. C.; Parra S.; Martínez P.; Tomás-Barberán F. A. The potent in vitro antioxidant ellagitannins from pomegranate juice are metabolised into bioavailable but poor antioxidant hydroxy-6H-dibenzopyran-6-one derivatives by the colonic microflora in healthy humans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2004, 43, 205–220. 10.1007/s00394-004-0461-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tomás-Barberán F. A.; González-Sarrías A.; García-Villalba R.; Nuñez-Sanchez M. A.; Selma M. V.; García-Conesa M. T.; Espin J. C. Urolithins, the rescue of ‘old’ metabolites to understand a ‘new’ concept; Metabotypes as a nexus between phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis and host health status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901 10.1002/mnfr.201500901. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

