Development of a cost-effective ovine antibody-based therapy against SARS-CoV-2 infection and contribution of antibodies specific to the spike subunit proteins
- PMID: 35533779
- PMCID: PMC9075985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105332
Development of a cost-effective ovine antibody-based therapy against SARS-CoV-2 infection and contribution of antibodies specific to the spike subunit proteins
Abstract
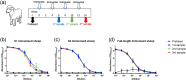
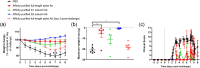
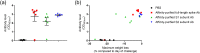
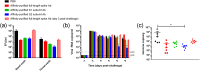
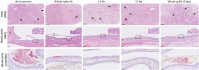
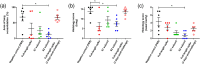
Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 are important to generate protective immunity, with convalescent plasma one of the first therapies approved. An alternative source of polyclonal antibodies suitable for upscaling would be more amendable to regulatory approval and widespread use. In this study, sheep were immunised with SARS-CoV-2 whole spike protein or one of the subunit proteins: S1 and S2. Once substantial antibody titres were generated, plasma was collected and samples pooled for each antigen. Non-specific antibodies were removed via affinity-purification to yield candidate products for testing in a hamster model of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies to whole spike, S1 and S2 proteins were evaluated for in vitro for neutralising activity against SARS-CoV-2 Wuhan-like virus (Australia/VIC01/2020) and a recent variant of concern, B.1.1.529 BA.1 (Omicron), antibody-binding, complement fixation and phagocytosis assays were also performed. All antibody preparations demonstrated an effect against SARS-CoV-2 disease in the hamster model of challenge, with those raised against the S2 subunit providing the most promise. A rapid, cost-effective therapy for COVID-19 was developed which provides a source of highly active immunoglobulin specific to SARS-CoV-2 with multi-functional activity.
Keywords: Antibodies; COVID-19; Development; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; Therapy.
Crown Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Sandra Smith and Neville Pope are employees of International Therapeutic Proteins Ltd. Gareth Humphries and Holger Schuhmann are employees of the Native Antigen Company. All other authors declare no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander F., Brunt E., Humphries H., Cavell B., Leung S., Allen L., Halkerston R., Lesne E., Penn E., Thomas S., Gorringe A., Taylor S. Generation of a universal human complement source by large-scale depletion of IgG and IgM from pooled human plasma. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022;2414:341–362. - PubMed
-
- Baum A., Fulton B.O., Wloga E., Copin R., Pascal K.E., Russo V., Giordano S., Lanza K., Negron N., Ni M., Wei Y., Atwal G.S., Murphy A.J., Stahl N., Yancopoulos G.D., Kyratsous C.A. Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies. Science. 2020;369(6506):1014–1018. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bewley K.R., Coombes N.S., Gagnon L., McInroy L., Baker N., Shaik I., St-Jean J.R., St-Amant N., Buttigieg K.R., Humphries H.E., Godwin K.J., Brunt E., Allen L., Leung S., Brown P.J., Penn E.J., Thomas K., Kulnis G., Hallis B., Carroll M., Funnell S., Charlton S. Quantification of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody by wild-type plaque reduction neutralization, microneutralization and pseudotyped virus neutralization assays. Nat. Protoc. 2021;16(6):3114–3140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

