Deciphering radiological stable disease to immune checkpoint inhibitors
- PMID: 35533926
- PMCID: PMC10001430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2022.04.450
Deciphering radiological stable disease to immune checkpoint inhibitors
Abstract
Background: 'Stable disease (SD)' as per RECIST is a common but ambiguous outcome in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). This study aimed to characterize SD and identify the subset of patients with SD who are benefiting from treatment. Understanding SD would facilitate drug development and improve precision in correlative research.
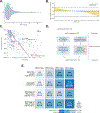
Patients and methods: A systematic review was carried out to characterize SD in ICI trials. SD and objective response were compared to proliferation index using The Cancer Genome Atlas gene expression data. To identify a subgroup of SD with outcomes mirroring responders, we examined a discovery cohort of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Serial cutpoints of two variables, % best overall response and progression-free survival (PFS), were tested to define a subgroup of patients with SD with similar survival as responders. Results were then tested in external validation cohorts.
Results: Among trials of ICIs (59 studies, 14 280 patients), SD ranged from 16% to 42% in different tumor types and was associated with disease-specific proliferation index (ρ = -0.75, P = 0.03), a proxy of tumor kinetics, rather than relative response to ICIs. In a discovery cohort of NSCLC [1220 patients, 313 (26%) with SD to ICIs], PFS ranged widely in SD (0.2-49 months, median 4.9 months). The subset with PFS >6 months and no tumor growth mirrored partial response (PR) minor (overall survival hazard ratio 1.0) and was proposed as the definition of SD responder. This definition was confirmed in two validation cohorts from trials of NSCLC treated with durvalumab and found to apply in tumor types treated with immunotherapy in which depth and duration of benefit were correlated.
Conclusions: RECIST-defined SD to immunotherapy is common, heterogeneous, and may largely reflect tumor growth rate rather than ICI response. In patients with NSCLC and SD to ICIs, PFS >6 months and no tumor growth may be considered 'SD responders'. This definition may improve the efficiency of and insight derivable from clinical and translational research.
Keywords: RECIST; immunotherapy/checkpoint blockade; lung cancer.
Copyright © 2022 European Society for Medical Oncology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure JL has received honoraria from Targeted Oncology and Physicians’ Education Resource. SW and QZ are former employees of AstraZeneca. MKC receives institutional research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb; and has received personal fees from Merck, InCyte, Moderna, ImmunoCore, and AstraZeneca. ANS reports advisory board positions with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Immunocore, Novartis, and Castle Biosciences; and institutional research support from BMS, Immunocore, Xcovery, Polaris, Novartis, Pfizer, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals, and Foghorn Therapeutics. MAP reports consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, Incyte, NewLink Genetics, Pfizer, and Aduro; honoraria from BMS and Merck; and institutional research support from Rgenix, Infinity, BMS, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and AstraZeneca. MHV reports receiving commercial research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Genentech/Roche; honoraria from Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb; travel/accommodation from Astra Zeneca, Eisai, Novartis, and Takeda; and consultant/advisory board member for Aveo, Calithera Biosciences, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Exelixis, Eisai, Merck, Onquality Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer. MSG has been a compensated consultant for Ultimate Opinions in Medicine LLC and MORE Health, Inc. AG and RR are employees of AstraZeneca. RR has a patent pending related to tumor mutation burden. MGK receives personal fees from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Daiichi-Sankyo; received honoraria for participation in educational programs from WebMD, OncLive, Physicians Education Resources, Prime Oncology, Intellisphere, Creative Educational Concepts, Peerview, i3 Health, Paradigm Medical Communications, AXIS, Carvive Systems, AstraZeneca, and Research to Practice; and received travel support from AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Genentech; is an employee of Memorial Sloan Kettering. Memorial Sloan Kettering has received research funding from The National Cancer Institute (USA), The Lung Cancer Research Foundation, Genentech/Roche, and PUMA Biotechnology for research conducted by MGK. MSK has licensed testing for EGFR T790M to MolecularMD. MDH, as of November 2021, is an employee of AstraZeneca; has received personal fees from Achilles, Adagene, Adicet, Arcus, Blueprint Medicines, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DaVolterra, Eli Lilly, Genentech/Roche, Genzyme/Sanofi, Janssen, Immunai, Instil Bio, Mana Therapeutics, Merck, Mirati, Natera, Pact Pharma, Shattuck Labs, and Regeneron; has options from Factorial, Shattuck Labs, Immunai, and Arcus; and has a patent filed by Memorial Sloan Kettering related to the use of tumor mutation burden to predict response to immunotherapy (PCT/US2015/062208), which has received licensing fees from PGDx. All other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Moertel CG, Hanley JA. The effect of measuring error on the results of therapeutic trials in advanced cancer. Cancer 1976; 38 (1): 388–394. - PubMed
-
- World Health O. WHO handbook for reporting results of cancer treatment. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1979.
-
- Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al. New Guidelines to Evaluate the Response to Treatment in Solid Tumors. JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2000; 92 (3): 205–216. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 2009; 45 (2): 228–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

