Molecular basis for cooperative binding and synergy of ATP-site and allosteric EGFR inhibitors
- PMID: 35534503
- PMCID: PMC9085736
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30258-y
Molecular basis for cooperative binding and synergy of ATP-site and allosteric EGFR inhibitors
Abstract
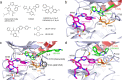
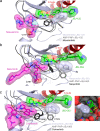
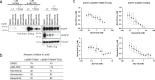
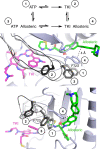
Lung cancer is frequently caused by activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Allosteric EGFR inhibitors offer promise as the next generation of therapeutics, as they are unaffected by common ATP-site resistance mutations and synergize with the drug osimertinib. Here, we examine combinations of ATP-competitive and allosteric inhibitors to better understand the molecular basis for synergy. We identify a subset of irreversible EGFR inhibitors that display positive binding cooperativity and synergy with the allosteric inhibitor JBJ-04-125-02 in several EGFR variants. Structural analysis of these complexes reveals conformational changes occur mainly in the phosphate-binding loop (P-loop). Mutation of F723 in the P-loop reduces cooperative binding and synergy, supporting a mechanism in which F723-mediated contacts between the P-loop and the allosteric inhibitor are critical for synergy. These structural and mechanistic insights will aid in the identification and development of additional inhibitor combinations with potential clinical value.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.J.E. is a consultant to Novartis, and the Eck laboratory receives or has received research funding from Novartis, Takeda, Sanofi, and Arbella. P.A.J. has received consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Takeda Oncology, ACEA Biosciences, Eli Lilly and Company, Araxes Pharma, Ignyta, Mirati Therapeutics, Novartis, LOXO Oncology, Daiichi Sankyo, Sanofi Oncology, Voronoi, SFJ Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Oncology, Transcenta, Silicon Therapeutics, Syndax, Nuvalent, Bayer, Esai, Biocartis, Allorion Therapeutics, Accutar Biotech and Abbvie; receives post-marketing royalties from DFCI owned intellectual property on EGFR mutations licensed to Lab Corp; has sponsored research agreements with AstraZeneca, Daichi-Sankyo, PUMA, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Revolution Medicines, and Astellas Pharmaceuticals; and has stock ownership in Gatekeeper Pharmaceuticals. N.S.G. is a founder, science advisory board member (SAB) and equity holder in Syros, C4, Allorion, Jengu, B2S, Inception, EoCys, Larkspur (board member) and Soltego (board member). The Gray lab receives or has received research funding from Novartis, Takeda, Astellas, Taiho, Jansen, Kinogen, Arbella, Deerfield, and Sanofi. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J. Clinicians. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Gridelli C, et al. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015;1:45–62. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA: Cancer J. Clinicians. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

