Ultrastructure of setae of a planktonic diatom, Chaetoceros coarctatus
- PMID: 35534511
- PMCID: PMC9085750
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11484-2
Ultrastructure of setae of a planktonic diatom, Chaetoceros coarctatus
Abstract
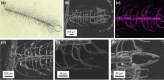
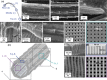
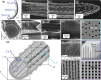
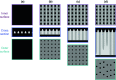
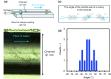
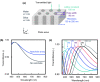
Silica frustules of most planktonic diatoms have many shallow holes in which the length (L) is smaller than the width (W). The present study focuses on a silica ultrastructure of setae of a planktonic diatom having deep (L/W > 1) holes. Here, we characterized microscopically patterned nanoholes on the silica walls of thick, robust, and hollow setae of a colony of Chaetoceros coarctatus. Basically, tetragonal poroid arrangements with and without a costa pattern are observed on the inner and outer surfaces, respectively, for three kinds of curving hollow setae attached to the anterior, intercalary, and posterior parts of the colony. The seta structures including specific poroid arrangements and continuity of deep nanoholes depend on the location. The deep nanoholes ∼90 nm wide are elongated from 150 to 1500 nm (L/W ∼17) with an increase in the wall thickness of the polygonal tubes of the setae. The inside poroid array, with a period of 190 nm in the extension direction of setae, is lined by parallel plates of the costae. However, the poroid arrangement on the outer surface is disordered, with several holes obstructed with increasing wall thickness of the posterior terminal setae. According to the movement of a colony in a fluid microchannel, the thick curving terminal setae is suggested to involve attitude control and mechanical protection. Using an optical simulation, the patterned deep through-holes on the intercalary setae were suggested to contribute anti-reflection of blue light in the wavelength range of 400 to 500 nm for the promotion of photosynthesis in seawater.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Losic D, Mitchell JG, Voelcker NH. Diatomaceous lessons in nanotechnology and advanced materials. Adv. Mater. 2009;21:2947–2958. doi: 10.1002/adma.200803778. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

