The value of Ki67 for the diagnosis of LSIL and the problems of p16 in the diagnosis of HSIL
- PMID: 35534530
- PMCID: PMC9085733
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11584-z
The value of Ki67 for the diagnosis of LSIL and the problems of p16 in the diagnosis of HSIL
Abstract
p16 and Ki67 are immunohistochemical markers related to cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions. p16 has been widely used to assist in the diagnosis of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. However, a conclusion about the role of Ki67 in the diagnosis of squamous intraepithelial lesions has not been established. The aim of this study was to analyze the role of p16 and Ki67 immunohistochemical staining in assisting cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions. This study performed immunohistochemical staining for p16 and Ki67 on 1024 cervical biopsy specimens at our hospital to compare the differences between p16 and Ki67 in different cervical lesions using the chi-squared test and Fisher's exact test. This study also evaluated the value of Ki67 for the diagnosis of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) using the receiver operating characteristic curve. The results indicated that Ki67 had high specificity and sensitivity in distinguishing LSIL from normal cervix. p16 was diffusely and strongly positive in some LSILs, and some problems were encountered in the interpretation of p16 staining. Therefore, we believe that Ki67 can be used as an immunohistochemical marker to help in the diagnosis of LSIL, to distinguish lesions that are difficult to morphologically determine and to avoid misdiagnosis. The practical application of p16 staining is still problematic. It may be necessary to find other auxiliary means to distinguish this small proportion of cervical lesions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
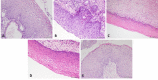

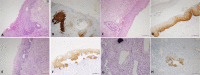
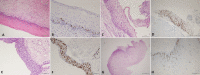
Similar articles
-
[The value of P16/ki67 double labeling, HPV E6/E7 mRNA detection and their combined application in cytological shunt diagnosis of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Jan;36(1):63-68. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32314725 Chinese.
-
[Significance of p16/Ki-67 double immunocytochemical staining in cervical cytology ASCUS, LSIL, and ASC-H].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Nov 25;52(11):734-739. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2017.11.004. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29179267 Chinese.
-
[The role of HPV E6/E7 mRNA combined with P16/ki67 immunocytochemistry in the diagnosis of atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance(ASCUS)].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Oct;34(10):937-941. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30554588 Chinese.
-
Efficiency of immunohistochemical p16 expression and HPV typing in cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion grading and review of the p16 literature.Pathol Res Pract. 2007;203(6):445-9. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2007.03.010. Epub 2007 May 31. Pathol Res Pract. 2007. PMID: 17543474 Review.
-
Role of Ancillary Techniques in Cervical Biopsy and Endocervical Curettage Specimens as Follow-Up to Papanicolaou Test Results Indicating a Diagnosis of Atypical Squamous Cells, Cannot Exclude High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion, or High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion.Acta Cytol. 2020;64(1-2):155-165. doi: 10.1159/000498888. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Acta Cytol. 2020. PMID: 30982025 Review.
Cited by
-
ADAR1 expression is associated with cervical cancer progression and negatively regulates NK cell activity.JCI Insight. 2025 Jul 8;10(13):e190244. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.190244. eCollection 2025 Jul 8. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 40626357 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of an on-chip p16ink4a/Ki-67 dual immunostaining cervical cytology system using microfluidic device technology.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 10;13(1):17052. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44273-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37816765 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Cervical Cancer Screening: Review of p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining as a Promising Triage Strategy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 19;14(4):451. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14040451. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relationship between Furin and Chronic Inflammation in the Progression of Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia to Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 7;15(19):4878. doi: 10.3390/cancers15194878. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835572 Free PMC article.
-
Significance and limitations of routine p16/Ki-67 immunohistochemistry as a diagnostic tool for high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix.Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2025 Jan;68(1):79-89. doi: 10.5468/ogs.24236. Epub 2024 Dec 18. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39690948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darragh TM, Colgan TJ, Cox JT, Heller DS, Henry MR, Luff RD, McCalmont T, Nayar R, Palefsky JM, Stoler MH, Wilkinson EJ, Zaino RJ, Wilbur DC, Members of LAST Project Work Groups The lower anogenital squamous terminology standardization project for HPV-associated lesions: Background and consensus recommendations from the College of American Pathologists and the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology. J. Low Genit. Tract Dis. 2012;16:205. doi: 10.1097/LGT.0b013e31825c31dd. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Niekerk D, Guillaud M, Matisic J, Benedet JL, Freeberg JA, Follen M, et al. p16 and MIB1 improve the sensitivity and specificity of the diagnosis of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions: Methodological issues in a report of 447 biopsies with consensus diagnosis and HPV HCII testing. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007;107:S233–S240. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.07.064. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Longatto Filho A, Utagawa ML, Shirata NK, Pereira SM, Namiyama GM, Kanamura CT, et al. Immunocytochemical expression of p16INK4A and Ki-67 in cytologically negative and equivocal pap smears positive for oncogenic human papillomavirus. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2005;24:118–124. doi: 10.1097/01.RCT.0000157092.44680.25. - DOI - PubMed

